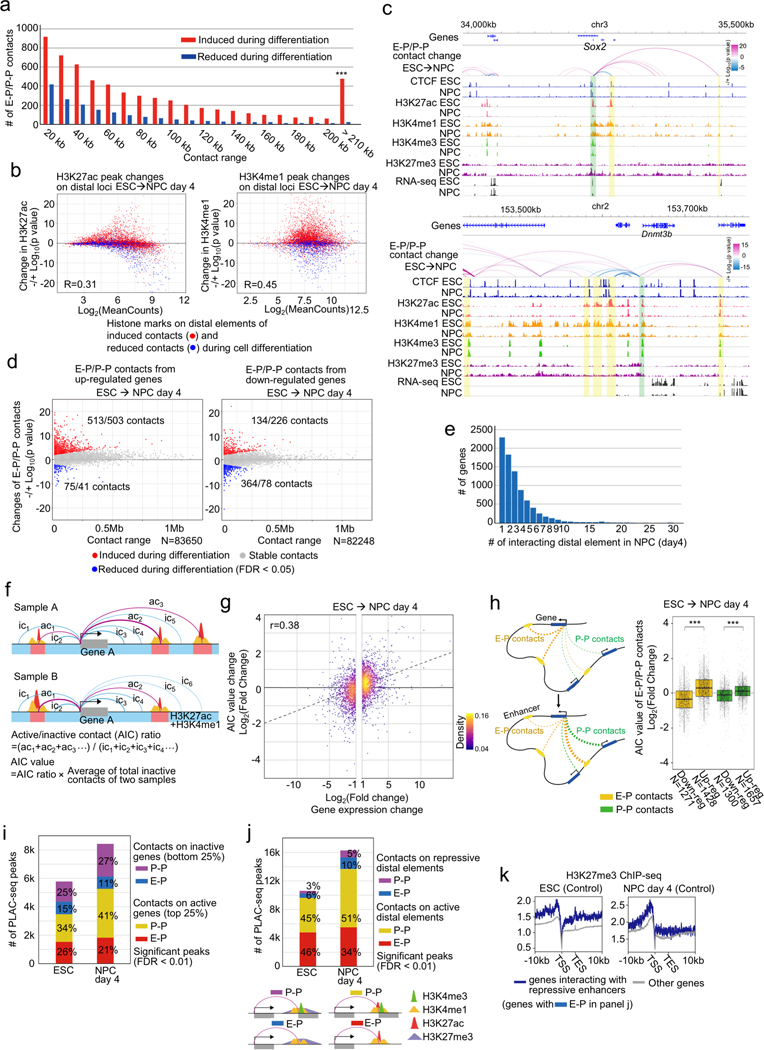
Extended Data Fig. 4. Features of E-P and P-P contacts that change during neural differentiation in control cells.
a, Histogram showing the number of significantly induced (red) and reduced (blue) E-P contacts between ESCs and NPCs and their genomic distances. *** p value < 0.001, Pearson’s Chi-squared test.
b, Scatter plots showing changes of H3K27ac and H3K4me1 ChIP-seq signals at distal elements that display significantly induced (red) or reduced (blue) E-P or P-P contacts during neural differentiation.
c, Genome browser snapshots of Sox2 (top) and Dnmt3b (bottom) loci. Arcs show changes of H3K4me3 PLAC-seq contacts on active elements and promoters between ESCs and NPCs (see Methods for details). The colors of arcs represent degrees of interaction change between samples (blue to red, −/+log10(p-value)) (Fisher’s exact test). Promoter regions of Sox2 and Dnmt3b and interacting enhancer regions are shown in green and yellow shadows, respectively. CTCF, H3K4me1, H3K27ac, H3K4me3, H3K27me3 ChIP-seq and RNA-seq in ESCs and NPCs (day 4) are also shown.
d, Scatter plots showing changes of E-P or P-P contacts anchored on up-regulated (left) and down-regulated (right) genes between ESCs and NPCs. Genomic distances between their two loop anchor sites are plotted on x-axis. Significantly induced and reduced chromatin contacts are shown as red and blue dots, respectively (FDR < 0.05).
e, Histogram showing the number of genes and the number of their interacting distal elements in NPCs. Genes without significant chromatin contacts were removed in this analysis.
f, Schematic representation of the AIC model to compute the correlation between changes of multiple E-P contacts and gene expression levels. H3K27ac and H3K4me1 peaks are shown as red and yellow peaks, respectively, and regions where these two types of peaks overlap are defined as active elements (red colored regions). Promoter-centered chromatin contacts on these active elements are shown as red arcs (active contacts) and other chromatin contacts are shown as blue arcs (inactive contacts). AIC ratio and value was calculated as indicated on the bottom (see Methods for details).
g, Scatter plots showing changes of AIC values and gene expression levels in differentially expressed genes during neural differentiation with linear approximation.
h, (Left) Schematic representation of a model to calculate AIC values using only P-P or E-P contacts. Promoter-centered chromatin contacts on active enhancers are shown as yellow arcs and chromatin contacts on other promoters are shown as green arcs. AIC ratios and values of P-P contacts and E-P contacts to other inactive contacts were calculated as shown in panel f. (Right) Box plots showing changes of the AIC values of P-P and E-P contacts in differentially expressed genes. The number of data points is indicated on the bottom. *** p value < 0.001, two-tailed t-test.
i, Histogram of the number of significant PLAC-seq peaks (FDR < 0.01) on P-P and E-P pairs anchored on active and inactive genes (top and bottom 25% of gene expression) in ESCs and NPCs.
j, Histogram showing the number of significant PLAC-seq peaks (FDR < 0.01) on P-P and E-P pairs anchored on active distal elements (presence of H3K4me1 and H3K27ac) and repressive distal elements (presence of H3K4me1 and H3K27me3, but not H3K27ac peaks) in ESCs and NPCs. Schematic representation of each type of chromatin contact is shown on the bottom.
k, Average enrichments of H3K27me3 ChIP-seq signals on TSSs and TESs of genes that interact with repressive distal enhancers identified in panel (j). H3K27me3 ChIP-seq signals on other genes are shown as control.