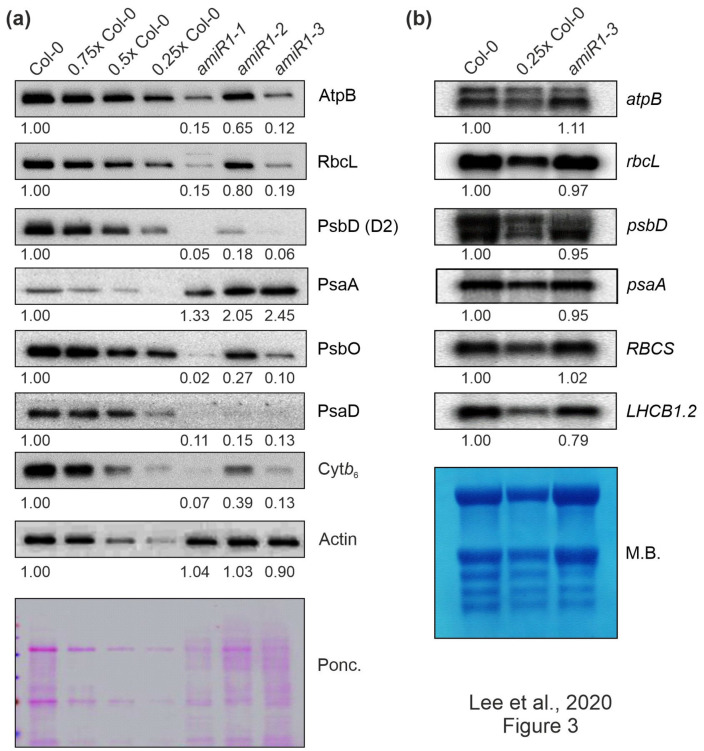
Figure 3.
The expression of chloroplast-encoded proteins is perturbed at the posttranscriptional level in mterf2 knock-down mutants. (a) Accumulation of chloroplast-encoded proteins in mterf2 knock-down mutants. Total leaf proteins were extracted from 6-day-old wild-type (Col-0) and amiRNA1-generated mterf2 mutants (amiR1), fractionated by SDS-PAGE, and blots were exposed to antibodies raised against individual photosynthetic proteins. Decreasing levels of wild-type proteins were loaded in the lanes marked Col-0, 0.75x Col-0, 0.5x Col-0, and 0.25x Col-0. Loading was adjusted to the fresh weights of leaf tissue. Actin detection and Ponceau Red (Ponc.)-staining of the blot served as loading controls. Quantification of signals relative to the wild type (= 1.00) is provided below each mterf2 mutant lane. (b) Steady-state transcript levels of photosynthetic genes in wild-type (Col-0) and amiR1–3 mutant seedlings. The total RNA was isolated from six-day-old wild-type and amiR1–3 seedlings, and aliquots (7 μg and 3.5 μg from the wild-type; 7 μg from amiR1–3) were resolved on a formaldehyde-containing denaturing gel, transferred onto a nylon membrane, and then probed with [α-32P]dCTP-labeled complementary DNA (cDNA) fragments that are specific for transcripts encoding individual subunits of PSII (psbD), PSI (psaA), ATPase-β (atpB), rbcL, rbcS, and LHCII (LHCB1.2). Ribosomal RNAs were visualized by staining the membrane with Methylene Blue (M. B.) which served as a loading control. Quantification of signals relative to the wild type (= 1.00) is provided below each amiR1–3 lane.