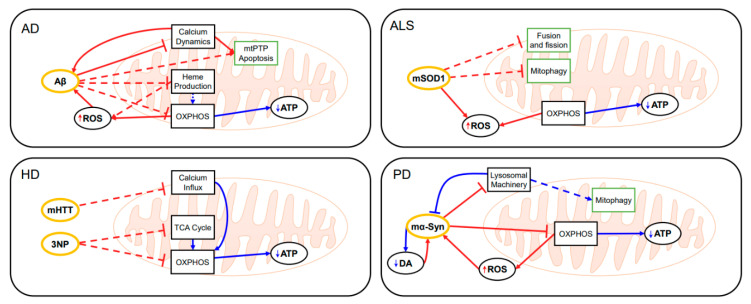
Figure 8.
Mitochondrial mechanisms of major neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), Huntington’s disease (HD), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Ovals and rectangles are molecules and pathways, respectively. Sharp/blunt arrows represent positive/negative interactions. Interactions that are enhanced in the disease condition are colored in blue, while the diminished are colored in red. Pathways in a single mitochondrion scale are colored in black and pathways in a population scale are colored in green. Interactions that have not been computationally modeled are represented in dashed lines. Aβ, amyloid-beta; ROS, reactive oxygen species; OXPHOS, oxidative phosphorylation; mtPTP, mitochondrial permeability transition pore; mα-Syn, mutant α-synuclein; DA, dopamine; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; mHTT, mutant huntingtin; 3NP, 3-nitropropionic acid; mSOD1, mutant superoxide dismutase 1.