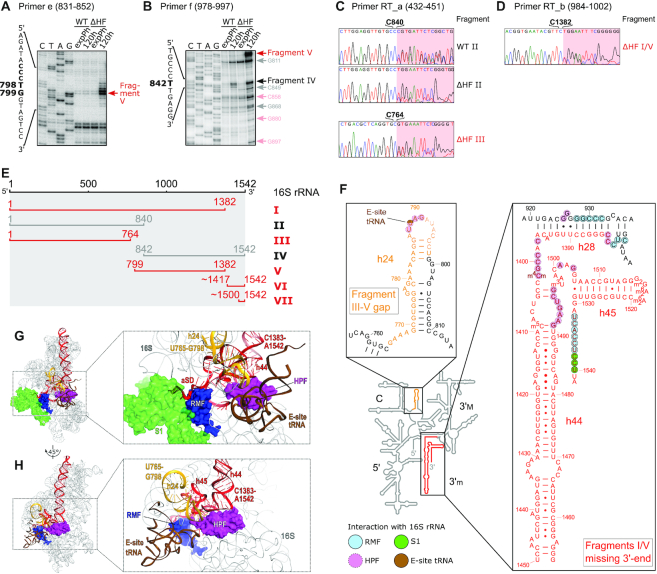
Figure 4.
Mapping of 16S rRNA fragments present in 70S ribosomes. (A, B) Primer extension analysis with RNA purified from 70S fractions of WT and HF cultures in exponential phase (expPh) and after 5 days of incubation (120 h), using primers e (panel A) and f (panel B). Red arrows indicate major 5′-ends that are exclusively present in ΔHF samples, black arrows indicate 5′-ends present in both WT and ΔHF samples. Light red and gray arrows mark additional 5′-ends in ΔHF and both strains, respectively. For full gels see Supplementary Figure S6. (C, D) RT-PCR analysis of RNA from samples described in (A, B). Shown are end sections of chromatograms obtained by sequencing with primer RT_a (C) and RT_b (D). Marked bases indicate the last base that could be assigned to 16S rRNA unambiguously. Red background indicates sequences corresponding to the 3′-linker used in the RT-PCR that are ambiguous due to a variable 3′-end of the fragment. For 3′-end sequencing workflow and extended results see Supplementary Figure S7. (E) Schematic summary of the mapped 16S rRNA fragments accumulating in 70S ribosomes after 5 days of starvation in MOPS MM. Red bars mark fragments exclusively or prevalently found in ΔHF-70S (fragments I, III, V and VI) or ΔHF-30S (fragment VII); gray bars mark fragments found in both WT- and ΔHF-70S (fragments II and IV). (F) Overlay of mapped degradation regions with the secondary structure of E. coli 16S rRNA (adapted from http://rna.ucsc.edu/rnacenter/images/figs/ecoli_16s.pdf). The 16S domains (5′ domain, 5′; Central domain, C; 3′ major domain, 3′M; 3′ minor domain, 3′m) are indicated. The gap between fragment I and III is coloured in orange; the missing 3′-terminus of fragments I and V is coloured in red. Inserts depict close-ups of selected regions. Light blue, magenta, green and brown background indicates residues that are interacting (according to Beckert et al. 2018) or in close proximity to RMF, HPF, ribosomal protein S1 or E-site tRNA in the 100S dimer, respectively. (G) 16S rRNA degradation sites in proximity to the binding site of RMF in the hibernating ribosome (PDB ID: 6H4N). The 3′-terminal region missing in fragments I and V (red) and h24 (orange) are in close proximity to RMF (dark blue) and ribosomal protein S1 (light green) at the mRNA exit channel and a tRNA in the E-site (brown). Inset shows close-up of the indicated region. Ribosomal proteins other than S1 have been omitted for the sake of clarity. (H) Top view of the 30S subunit of the hibernating ribosome with bound HPF (magenta) (PDB ID: 6H4N) interacting with h44, h45 and h24. Colour scheme as in (G).