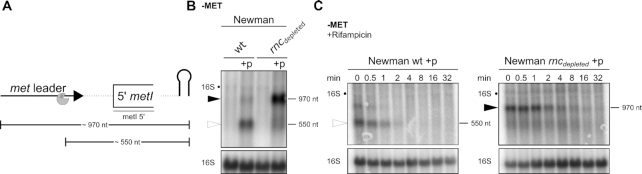
Figure 9.
RNase III cleavage of terminator stem facilitates 5′ met operon mRNA exonucleolytic degradation. (A) Scheme of transcripts detected in (B); met leader sequence depicted as thick, black arrow, first 215 nt of metI shown as open rectangle, plasmid-derived transcription terminator shown as hairpin. Line below metI indicates relative position of the probe used in (B) and (C). RNase III cleavage site is shown as pac-man. Approximate transcript sizes are given below the scheme. (B) Total RNA was isolated from S. aureus Newman, its isogenic RNase III (rncdepleted) mutant and from both strains transformed with the plasmid (‘+p’) detailed in Figure 8A grown in CDM without methionine (‘−MET’). RNA was run on an agarose gel. Northern blot was probed with a metI 5′-specific probe. Open arrowhead marks ∼550 nt transcript and black arrowhead marks ∼970 nt transcript. Approximate transcript lengths are indicated on the right of the blot. Re-hybridization with a 16S rRNA-specific probe was used as loading control. (C) Total RNA was isolated from S. aureus Newman and its isogenic RNase III (rncdepleted) mutant strain transformed with the plasmid (‘+p’) grown in CDM without methionine (‘−MET’) over a time course after rifampicin addition (0–32 min). RNA was run on an agarose gel. Hybridization and labelling as described for (B).