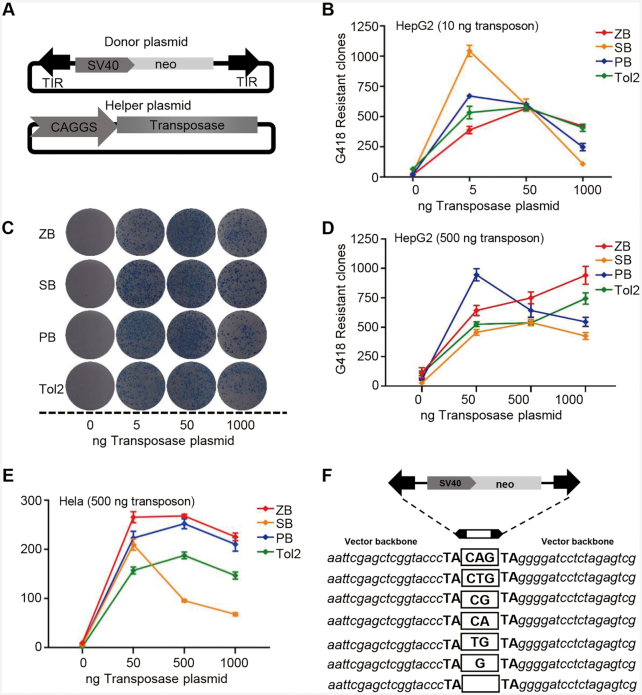
Figure 2.
Transposition activities of ZB, SB, PB and Tol2 in human cells. (A) Donor and helper plasmids used in human cells. Donor plasmids: the arrows represent transposon terminal inverted repeats (TIRs); SV40, SV40 promoter; neo, neomycin resistance gene. Helper plasmids: CAGGS, CAGGS promoter; transposase, the transposase (ZB, PB, SB, or Tol2) coding gene. (B) Comparative transposition activities of ZB, SB, PB and Tol2 in HepG2 cells co-transfected with low transposon DNA conditions (10 ng). (C) Stable colonies from HepG2 cells co-transfected with ZB, SB, PB and Tol2 transposons in low transposon DNA conditions (10 ng). (D–E) Comparative transposition activities in HepG2 and HeLa cells co-transfected with the ZB, SB100X, PB and Tol2 transposons in high transposon DNA conditions (500 ng). (F) Excision footprint of ZB. A schematic representation of the donor is shown on top. The pUC19 vector backbone sequences that flank the element in the donor construct are shown in italics. The transposon footprints are depicted in the white box.