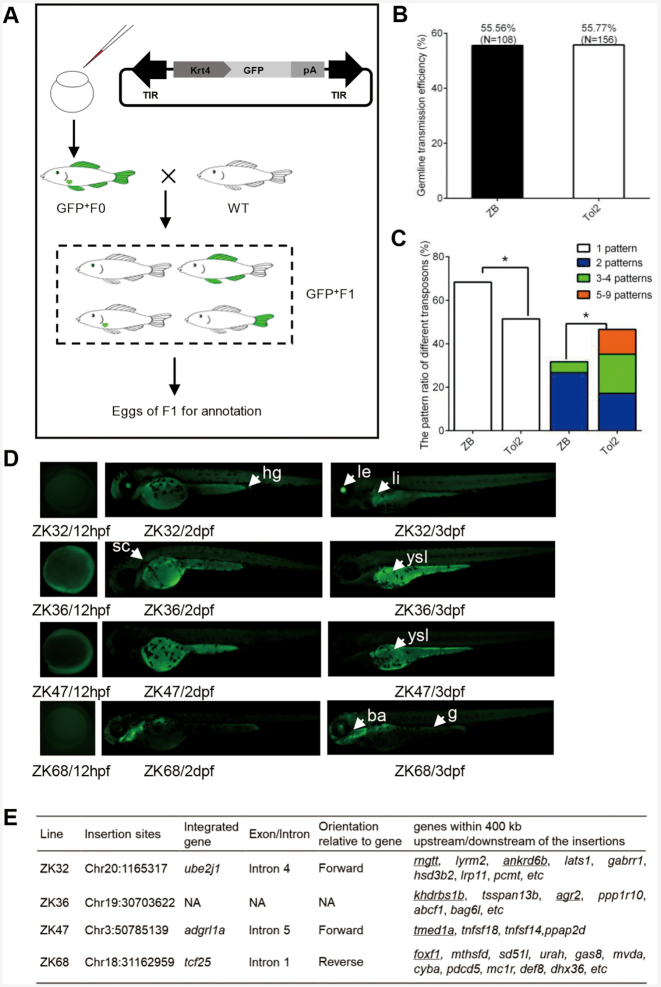
Figure 4.
ZB transposon as a transgenic tool in zebrafish. (A) ET constructs used in zebrafish. The arrows represent transposon TIRs; Krt4, Krt4 minimal promoter; GFP, reporter (green fluorescent protein) gene; pA, β-globin polyA. (B) Comparison of germline transmission efficiency mediated by the ZB and Tol2 transposons by screening GFP expression in the F1 generation. (C) Different GFP patterns of F1 offspring generated from ZB- and Tol2-mediated transgenic zebrafish. (D) Fluorescence microscopy images of four ET lines from ZB-mediated transgenic zebrafish at 12 hpf, 2 dpf and 3 dpf. The arrows and arrowheads indicate distinct expression domains with resemblance to the activity of genes in the landing site environment. Abbreviations: ba, branchial arches; sc, spinal cord; g, gut; hg, hindgut; le, lens; li, liver; ysl, yolk syncytial layer. (E) Insertion sites of four ET lines. The predicted target genes that are expressed in similar domains to that shown by the ET lines are underlined.