Figure 5.
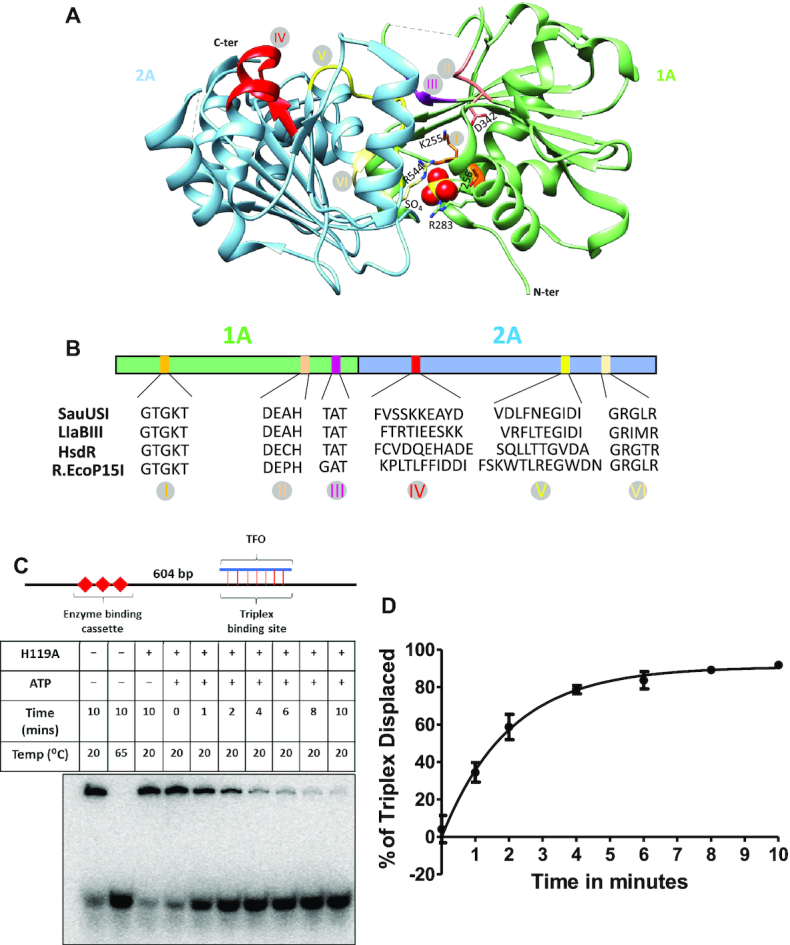
ATPase-driven DNA translocation by SauUSI. (A) The primary domain architecture of the SF2-helicase like ATPase along with the canonical motifs marked in specific colors. The canonical motifs of the SF2-helicase like ATPase of SauUSI are compared to that of LlaBIII (Type ISP REase), HsdR (Type I REase) and EcoP15I (Type III REase). (B) Structure of the ATPase domain with the two RecA folds colored distinctly. The catalytically important Walker A and Walker B residues, along with a sulfate ion (shown as a sphere) bound at the ATP binding site are shown. Also, illustrated are the other canonical motifs in the same color code as in panel A. (C) The DNA used for the triplex displacement assay has an enzyme binding cassette located 604 bp away from the triplex binding site. A representative PAGE gel of the triplex displacement assay carried out over a time period of 1–10 min. (D) Translocase activity of SauUSIH119A monitored by the percentage of triplex displaced as a function of time (n = 3).
