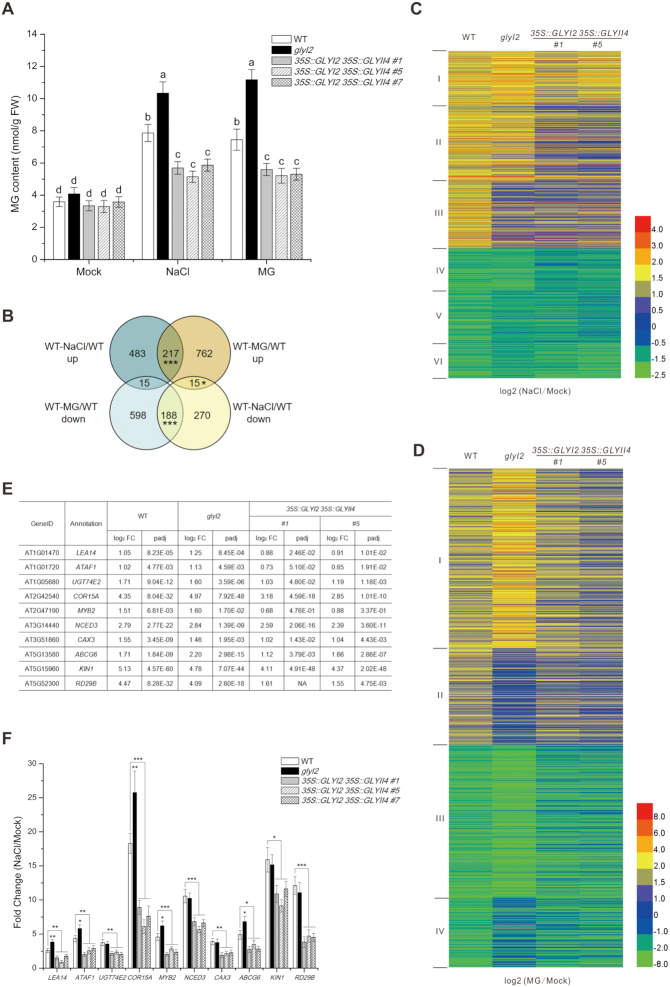
Figure 1.
MG regulates salt stress responsive gene expression. (A) MG content in 5-day-old wild-type, glyI2, and 35S::GLYI2 35S::GLYII4 seedlings treated or not with 100 mM NaCl or 200 μM MG for 12 h. Data are means ± SD of three independent biological replicates. Different letters indicate significant differences between the annotated columns (P < 0.05 by Tukey's test). FW, fresh weight. (B) Venn diagrams representing the numbers of transcripts upregulated or downregulated by more than 2-fold, with genes shared between treatments overlapping. RNA-seq analysis of 5-day-old wild-type (WT) seedlings treated or not with 100 mM NaCl or 200 μM MG for 12 h. WT-NaCl/WT (NaCl-treated WT relative to WT), WT-MG/WT (MG-treated WT relative to WT). Significant level for the elements in common determined by Fisher's exact test: *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. (C and D) Hierarchical clustering of transcripts up- or down-regulated 2-fold or more in wild-type plants under NaCl (C) and MG (D) treatment, and fold changes of these transcripts in glyI2 and 35S::GLYI2 35S::GLYII4 plants. NaCl/Mock (NaCl-treated plants relative to untreated plants), MG/Mock (MG-treated plants relative to untreated plants). (E and F) Expression levels of salt stress responsive genes assayed by RNA-seq (E) and RT-qPCR (F) in 5-day-old wild-type, glyI2 and 35S::GLYI2 35S::GLYII4 seedlings treated or not with 100 mM NaCl for 12 h. FC (fold change of gene expression in NaCl-treated plants relative to untreated plants). Data are means ± SD of three independent biological replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences in comparison with the wild type (Student's t-test): *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.