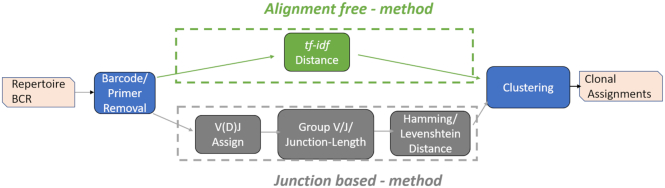
Figure 1.
A flow diagram depicting the major steps for identifying clonally-related B cell receptor sequences (bottom row). Given a set of BCR sequences (the repertoire), first, the primers and barcodes are removed, then V(D)J genes are assigned based on an alignment of the sequences to a database of germline genes. Sequences are grouped based on V and J gene assignments and junction length. A hamming distance is calculated on the junction regions of pairs of sequences in each of the groups separately. Finally, distances are fed into a clustering algorithm (Hierarchical (14) or Spectral (15)). Here, we propose to use a tf-idf based distance that bypasses the three steps prior to clustering, and is not restricted to sequences with the same V or J gene or junction length.