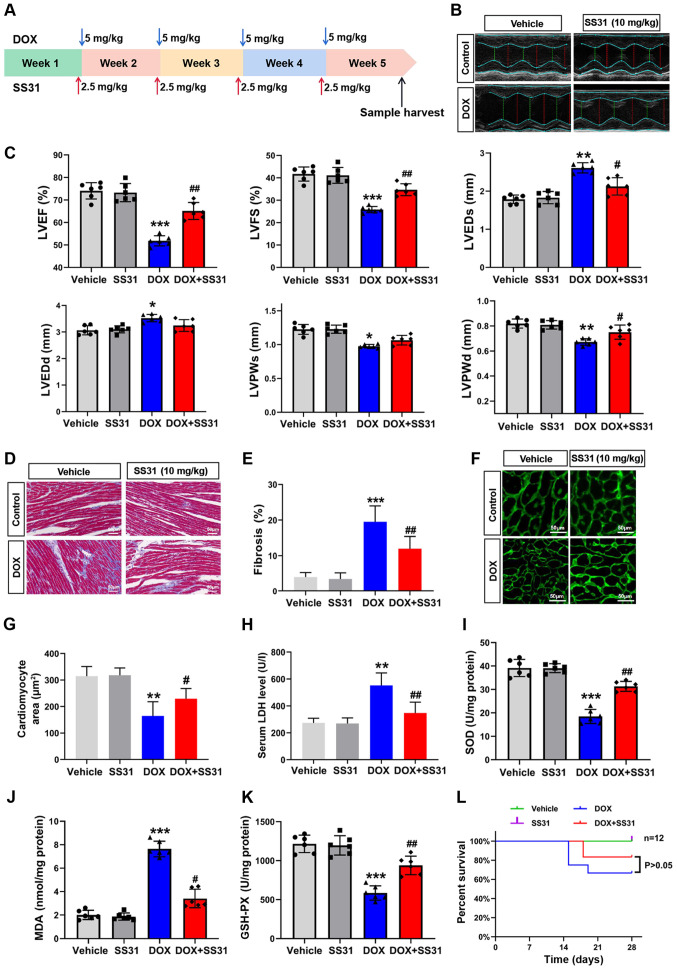
Figure 4.
Effects of SS31 on DOX-induced cardiac injury in vivo. (A) Timeline of the experimental procedure for the DOX-induced mouse cardiotoxicity model. (B) Representative photographs of the echocardiography analysis. (C) Quantified data of the echocardiography analysis. (D) Masson trichrome staining. Magnification, ×400. (E) Quantitative analysis of fibrosis in the Masson-stained sections. (F) Representative photographs of wheat germ agglutinin staining. Magnification, ×400. (G) Quantitative analysis of the cardiomyocyte area. (H) Serum LDH levels. n=6 mice/group. (I-K) SOD, MDA and GSH-PX levels were evaluated in mouse heart tissue samples. n=6 mice/group. (L) Survival of mice following DOX-induced cardiac injury. Day 0 refers to the first DOX injection. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 vs. vehicle; #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01 vs. DOX. DOX, doxorubicin; SS31, Szeto-Schiller 31 peptide; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; SOD, superoxide dismutase; MDA, malondialdehyde; GSH-PX, glutathione peroxidase; EF, ejection fraction; FS, fractional shortening; LVEDs, left ventricular end-systolic diameter; LVEDd, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter; LVESV, left ventricular end-systolic volume; LVEDV, left ventricular end-diastolic volume.