Figure 4.
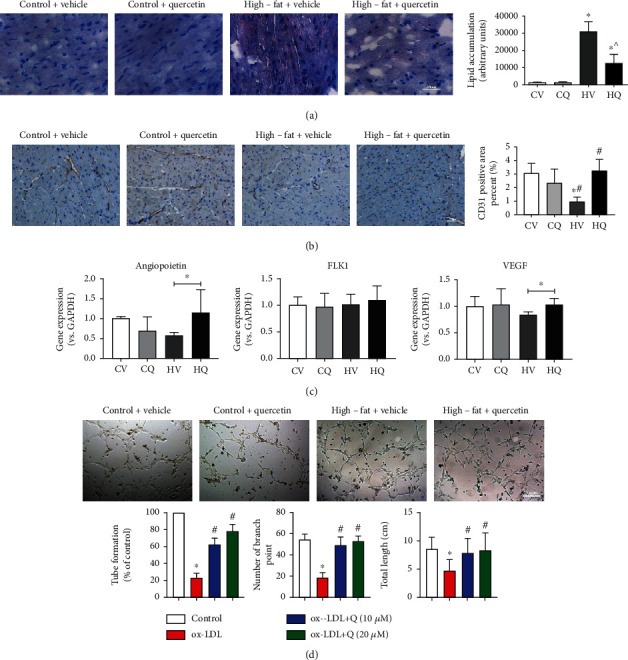
High-fat diet (HFD) elicits lipid accumulation and vascular rarefaction in the myocardium of C57BL/6J mice, which quercetin (Q) alleviated. (a) Accumulation of Oil-red-O-stained lipid droplets in the heart after HFD, which Q blunted. Control+vehicle (CV; n = 5); control+quercetin (CQ; n = 5); high-fat+vehicle (HV; n = 6); high-fat+quercetin (HQ; n = 5); (b) Decreased area of CD31 + staining in the HFD heart was improved by Q. Data are mean ± standard deviation. CV, n = 7. CQ, n = 6. HV, n = 5. HQ, n = 6. ∗P < 0.05 vs. CV. #P < 0.05 vs. CQ. ^P < 0.05 vs. HV. (c) Expression of angiopoietin and VEGF increased in the HFD myocardium after Q treatment. CV, n = 8. CQ, n = 8. HV, n = 6. HQ, n = 8. ∗P < 0.05. (d) Effect of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) and Q on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) tube formation. Representative microphotographs show that Q improved tube formation. ∗P < 0.05 vs. control; #P < 0.05 vs. ox-LDL.
