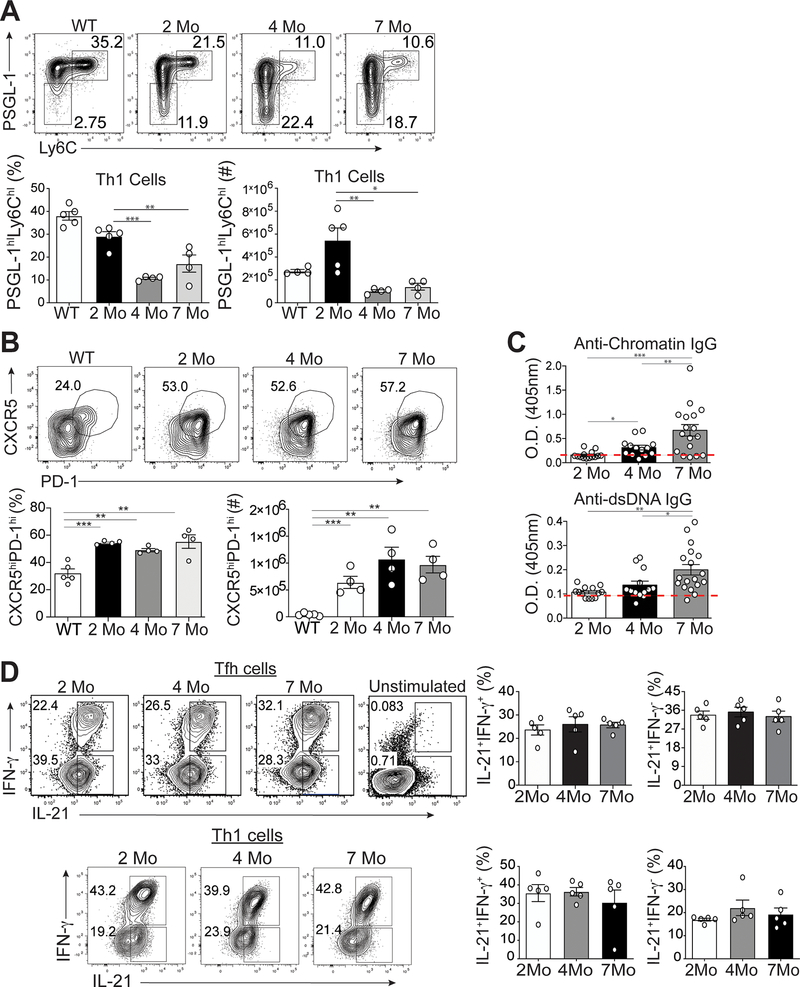
Figure 1.
Temporal formation of Tfh and Th1 cells during different stages of disease. Spleens were harvested from either B6.Sle1.Yaa at 2, 4, and 7 months of age or control 2 months of age wild type B6 mice. (A) Representative flow cytometry plots of Ly6chiPSGL-1hi Th1 cells from B6.Sle1.Yaa mice with percentages and numbers of cells (bottom left and right, respectively) (B) Representative flow cytometry plots of CXCR5hiPD-1hi Tfh cells from B6.Sle1.Yaa mice with percentages and numbers cells (bottom left and right, respectively). (C) Anti-Chromatin IgG (left), and Anti-IgG antibodies (right) in sera of mice B6.Sle1.Yaa at 2, 4, and 7 months of age, with a dashed line representing the average O.D. from 6-month-old wild type B6 mice. (D) Intracellular IL-21 and IFN-γ staining in Tfh cells (top) and Th1 cells (bottom) with percentages (right) of cytokine-positive cells. Cytokine positive cells gates were based on unstimulated Tfh cells (top right). Data are representative of 3 experiments with 3–5 mice per group. ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05 by Student’s t-test. Error bars represent SEM.