Figure 1. Effect of iloprost on VE-cadherin localization and cell permeability.
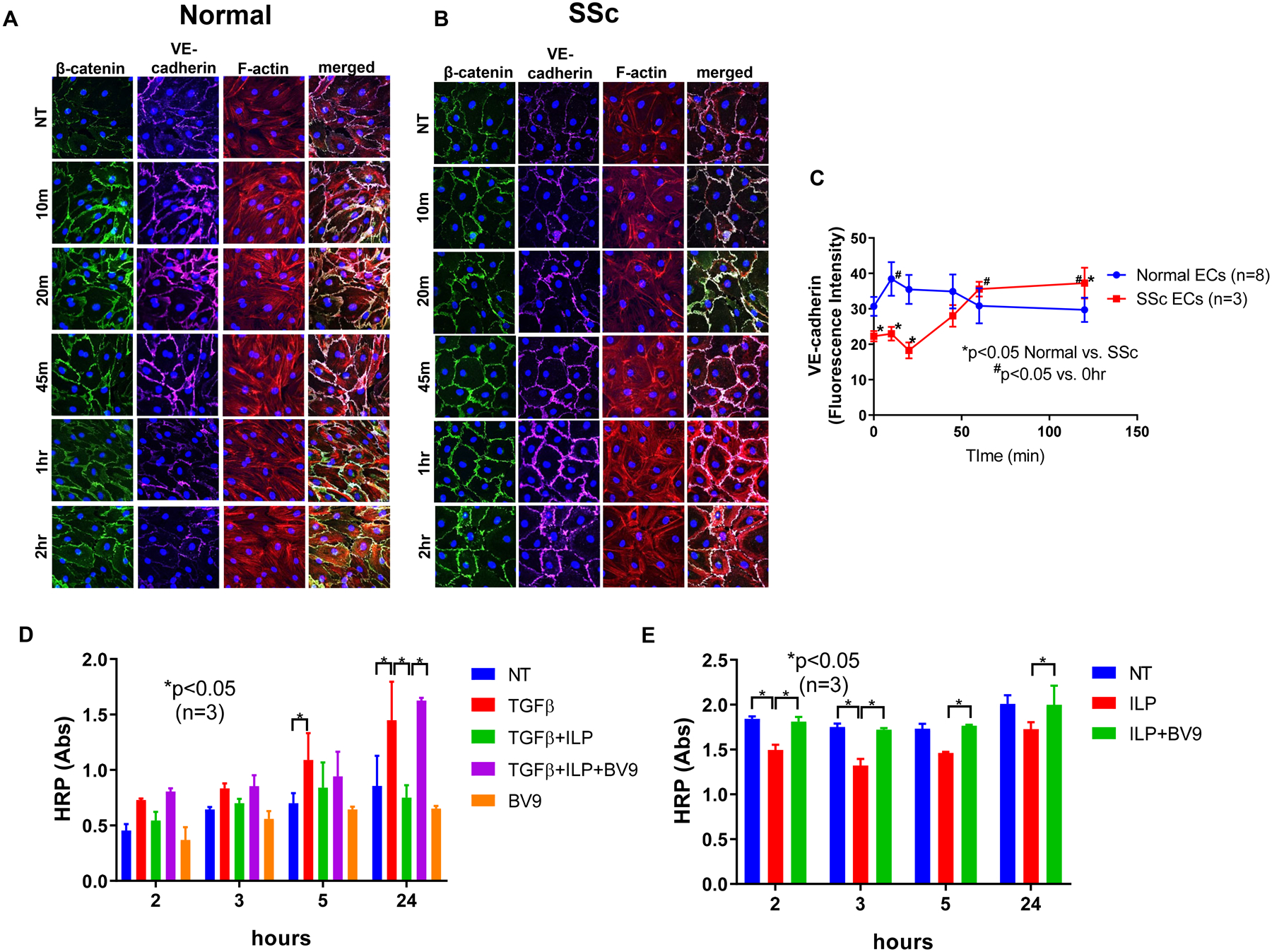
Immunofluorescence of VE-cadherin, β-catenin, and F-actin in ECs were visualized using a Nikon A1 confocal microscope and pictures were taken at 600x. Cell permeability was assessed by measuring HRP movement through EC monolayers using the Endothelial Transwell Permeability Assay Kit. Cells were treated with iloprost (150nM) and/or TGFβ (10ng/ml) at various time points. BV9 (25 μg/ml) was used to pre-treat the cells for 30 min before iloprost and TGFβ were added. (A) Iloprost increased junctional clustering of VE-cadherin and β-catenin as soon as 10 min of incubation in normal ECs; (B) Iloprost showed a delayed but more prolonged effect on VE-cadherin and β-catenin clustering in SSc ECs. Disorganized F-actin filaments in SSc ECs were also observed; (C) Quantification of fluorescent signal of VE-cadherin showed significant reduction of VE-cadherin in SSc ECs compared to normal ECs at baseline. After iloprost, VE-cadherin intensity was greater in SSc compared to normal ECs; (D) In normal ECs, TGFβ increased permeability as measured by HRP movement through EC monolayers. Iloprost inhibited permeability of EC monolayers while blockade of VE-cadherin by BV9 reversed it. (E) In SSc ECs, iloprost inhibited the increased permeability of these cells while the function blocking antibody to VE-cadherin (BV9) prevented the effects of iloprost. Experiments were done with at least 3 subject-derived lines. Results are expressed as mean +/− SD and p<0.05 was considered significant. NT: not treated; ILP: iloprost; Abs: absorbance
