Figure 4. Vascular protective effect of iloprost in SSc.
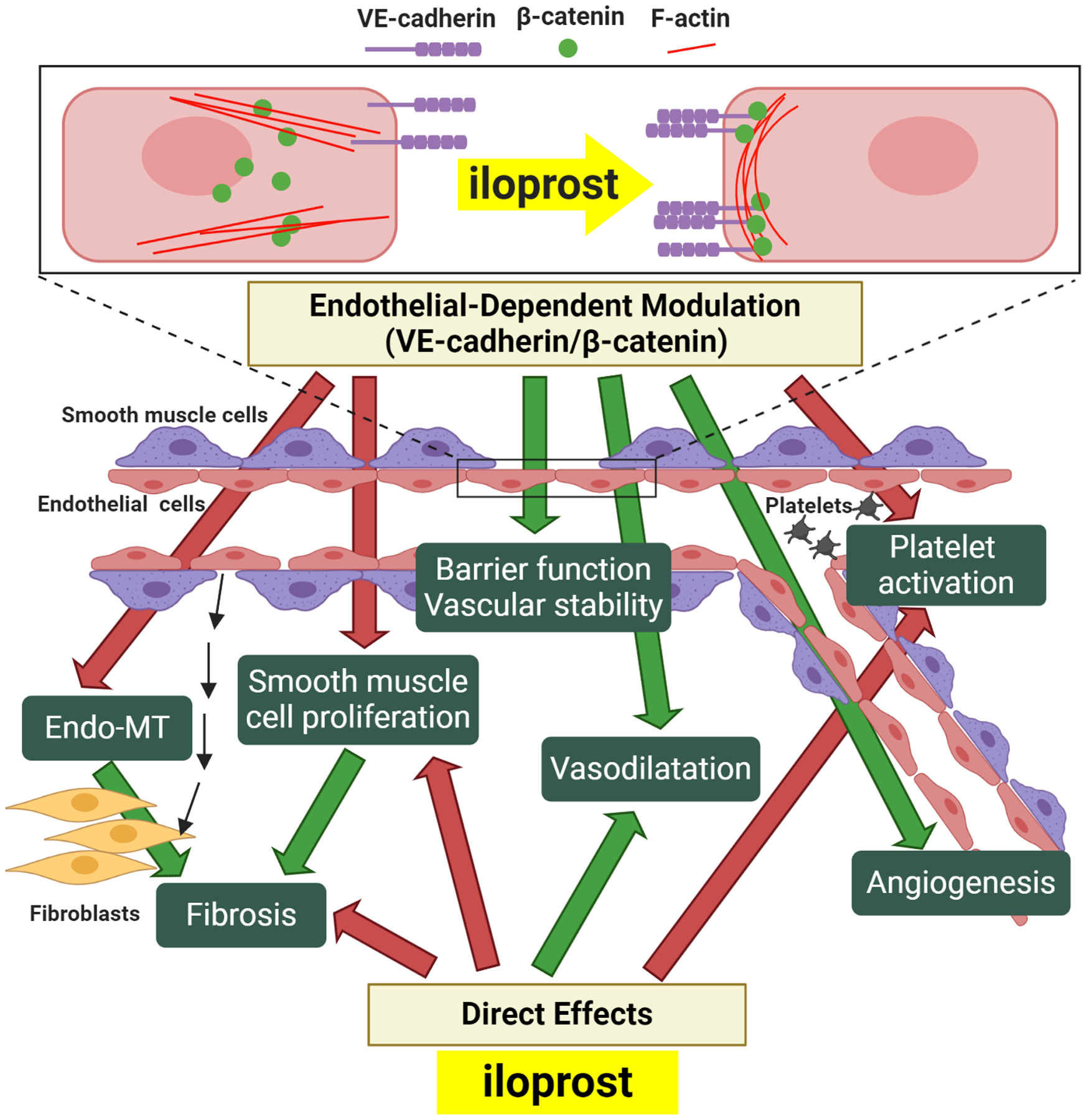
In SSc ECs, Iloprost increases VE-cadherin and β-catenin clustering at the adherens junction, accompanied with accumulation of peripheral F-actin. Increased interaction and signaling of VE-caderin/β-catenin will promote protective endothelial functions and vascular stability including an increase in barrier function, promotion of angiogenesis, inhibition of Endo-MT, and increased NO activity, which will contribute to vasodilation, inhibition of platelet activation, and blockade of smooth muscle cell proliferation. Endo-MT and smooth muscle proliferation can contribute to intravascular and extravascular fibrosis, and to microvascular rarefaction. In addition to these endothelial-dependent modulatory effects, iloprost can also act directly on platelets, fibroblasts, and smooth muscle cells to inhibit platelet activation and fibrosis, and promote vasodilation. Inhibitory effects are highlighted by red arrows, and positive effects are highlighted with green arrows.
