Figure 1. Ca2+ flux into the mitochondria through global cytoplasmic Ca2+ and Ca2+ microdomains.
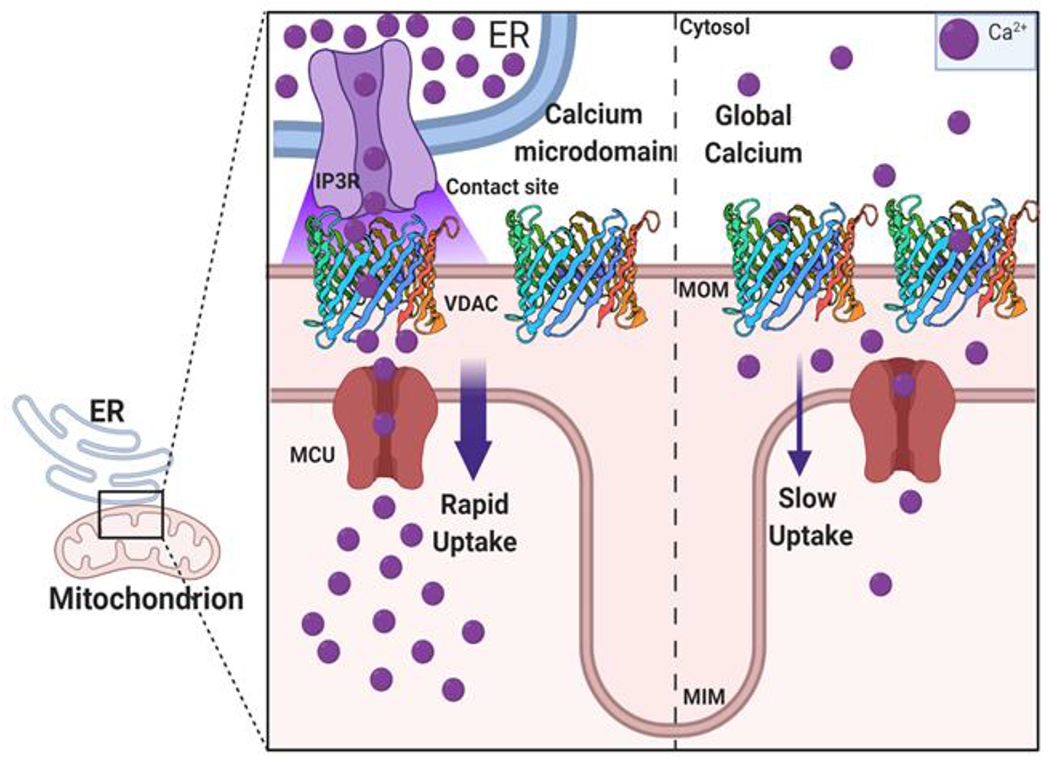
Mitochondria interact with organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) through contact sites generating Ca2+ microdomains. These Ca2+ microdomains (left half), contain a multi-protein complex linking IP3R (an ER Ca2+ channel in purple) to VDAC (3D structure representation) in the mitochondrial outer member (MOM). The microdomains enable rapid transfer of Ca2+ (Ca2+ sparks) from the ER to mitochondria through VDAC and the MCU in the inner membrane (MIM). Global or capacitive uptake of Ca2+ from the cytosol (right half) is slower due to the lower local concentration of Ca2+compared to microdomains. Ca2+enters the cytosol from extracellular space or ER stores.
