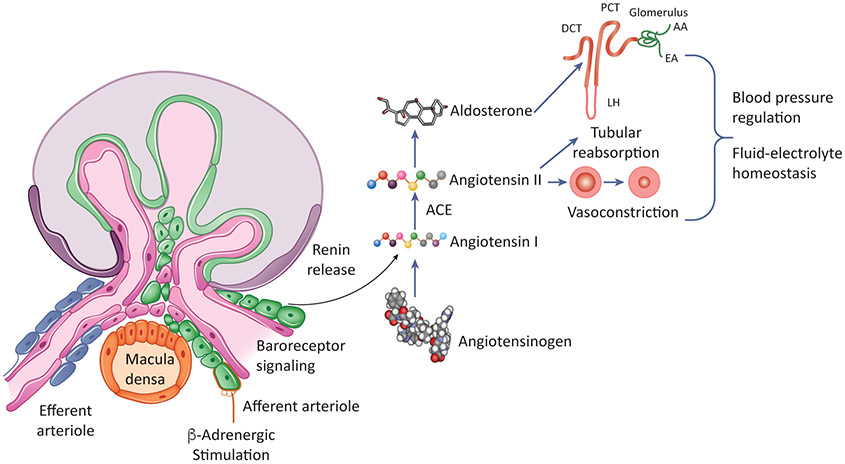
Figure 1: The-Renin Angiotensin-System.
The rate-limiting step of this cascade involves the secretion of renin from juxtaglomerular cells in response to sympathetic stimulation, changes in perfusion pressure and salt levels in the urinary system. Renin, a hormone enzyme, cleaves angiotensinogen into angiotensin I, an inactive deca-peptide. Angiotensin I is further processed into angiotensin II by angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) to produce angiotensin II. Angiotensin has a critical role in restoring homeostasis namely by inducing vasoconstriction to increase blood pressure and stimulating the adrenal gland to produce aldosterone which promotes sodium re-uptake in the kidney. Together, these actions regulate blood pressure and fluid-electrolyte balance, thus restoring homeostasis.