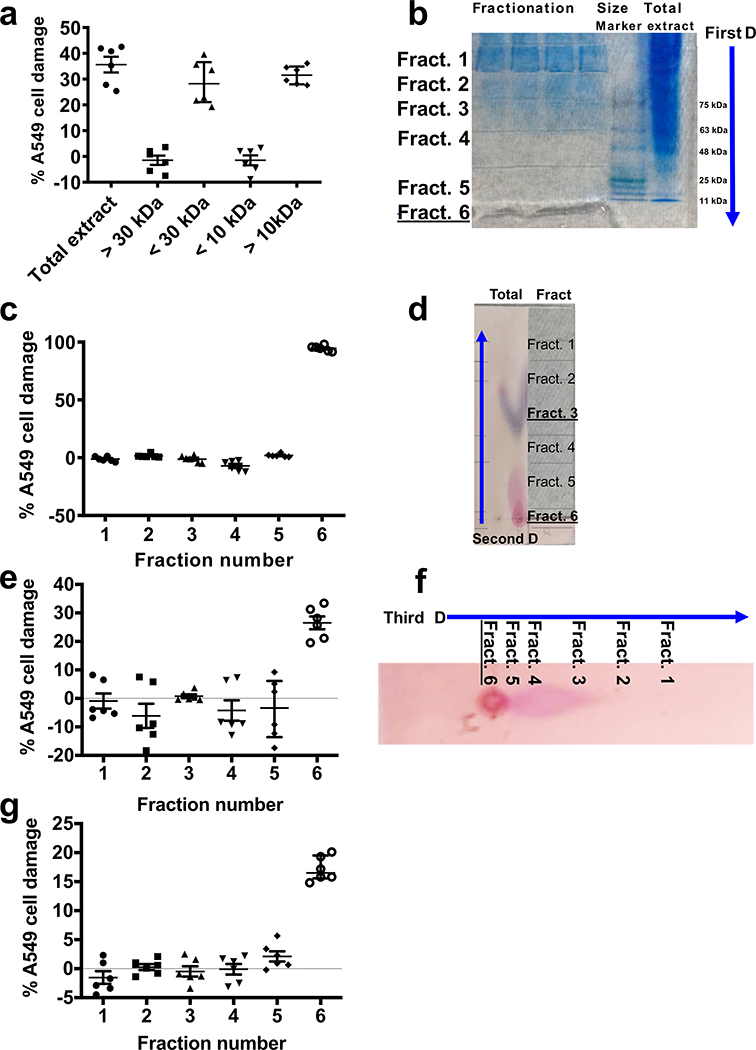
Extended Data Fig. 2. Fractionation and purification of R. delemar toxin.
(a) Size exclusion of hyphae extracts indicating a 10–30 kDa fraction causing A549 cell damage (n=6 wells/fraction, pooled from three independent experiments). Data are median ± interquartile range. (b) Native polyacrylamide fractionation of hyphae extract and (c) its corresponding A549 cell damage, showing fraction # 6 causing injury. (n=6 wells/fraction, pooled from three independent experiments). Data are median ± interquartile range. (d) Cellulose plate separation of fraction # 6 purified from the polyacrylamide gel and (e) its corresponding A 549 cell damage, showing a high polar fraction #6 causing injury. Data are n=6 wells/fraction, and pooled from three independent experiments. Data are median ± interquartile range. (f) Third dimension fractionation of the previous fraction # 6 on cellulose plates and (g) its corresponding A549 cell injury (n=6 wells/fraction, pooled from three independent experiments). Data are median ± interquartile range.