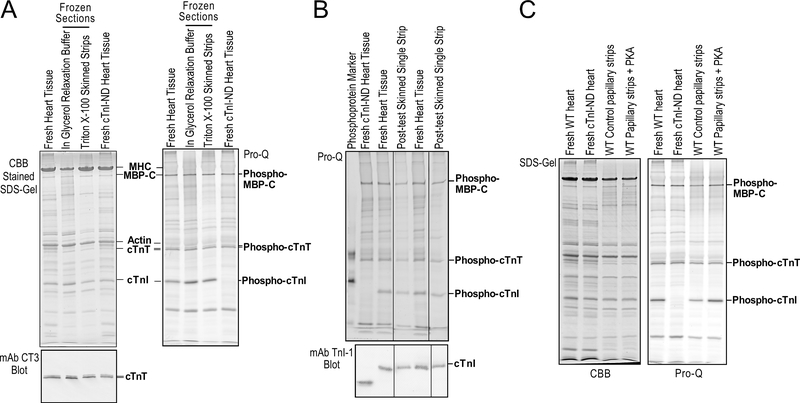
Figure 6. Preserved integrity and phosphorylation state of myofilament proteins in cryosection-generated skinned cardiac muscle strips.
(A) Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) and ProQ phosphoprotein stained SDS-PAGE gels and mAb CT3 Western blot showed the protein profiles of cryosection-generated skinned papillary muscle strips prior to and post skinning. In comparison with fresh papillary muscle homogenate control, the results demonstrate preserved integrity of myofilament proteins, myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin binding protein C (MBP-C), actin, cardiac TnT (cTnT) and cardiac TnI (cTnI) and in vivo phosphorylation state of MBP-C, cTnT and cTnI. Transgenic mouse heart contains solely N-terminal phosphorylation sites deleted cTnI (cTnI-ND) was used as a control of non-phosphorylated cTnI. (B) The protein samples recovered from skinned papillary muscle strips after contractility experiments were sufficient for SDS-PAGE, phosphoprotein staining, and Western blotting analysis. The Pro-Q stained SDS-gel and mAb TnI-1 Western blots demonstrate that the cryosection-generated skinned cardiac muscle strips preserved the native state of myofilament protein phosphorylation as shown by that of MBP-C, cTnT and cTnI together with cTnI-ND control. (C) PKA treatment of cryosection-generated skinned cardiac muscle strips from a mouse heart after ex vivo perfusion to diminish the effective of systemic adrenergic tune and lower baseline level of myofilament phosphorylation produced significant and specific increases in the phosphorylation of MBP-C and cTnI, indicating preserved myofilament structure for posttranslational physiologic regulations. Fresh cardiac muscles of wild type and cTnI-ND mice were used as controls.