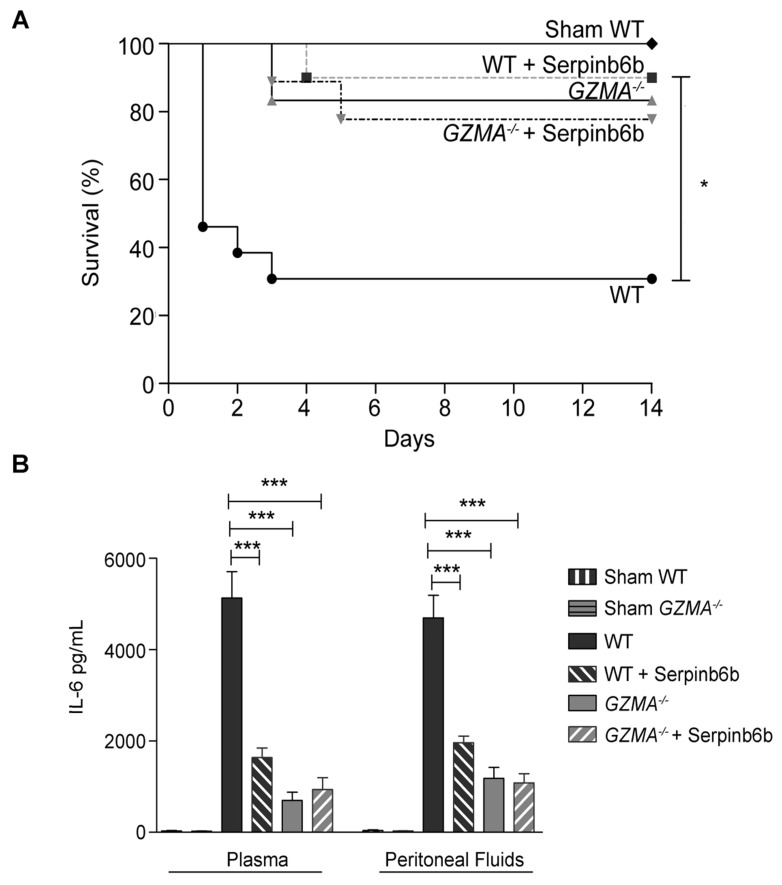
Figure 6.
Inhibition of extracellular GzmA improves sepsis outcome and reduces inflammation. Sepsis was induced by CLP in B6 and GZMA-/- mice as described in materials and methods. Immediately after surgery mice were treated with 40 µg of Serpinb6b in 100 µl of PBS (10 WT and 9 GZMA-/- mice). This treatment was repeated 6 h later and once a day during 5 days. Control mice received only 100 µl of PBS i.p. (13 WT and 6 GZMA-/- mice). After 6 h a mixture of antibiotics, ceftriaxone (30 mg/kg) + metronidazole (12.5 mg/kg) was administered i.p. once a day for 5 days. WT sham operated mice (4 WT mice) underwent the same procedure but without the ligation and puncture of the cecum. (A) Survival was monitored during 14 days. The data correspond to the indicated number of mice combined from two independent experiments. Statistical analyse was performed using logrank and Gehan-Wilcoxon test. *p < 0.05. (B) 24 h after sepsis induction mice were sacrificed and the levels of IL-6 in plasma and peritoneal fluids was determined by ELISA. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of 4 (Sham) or 6 (CLP) biological replicates from 2 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA test with Bonferroni's post-test *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.