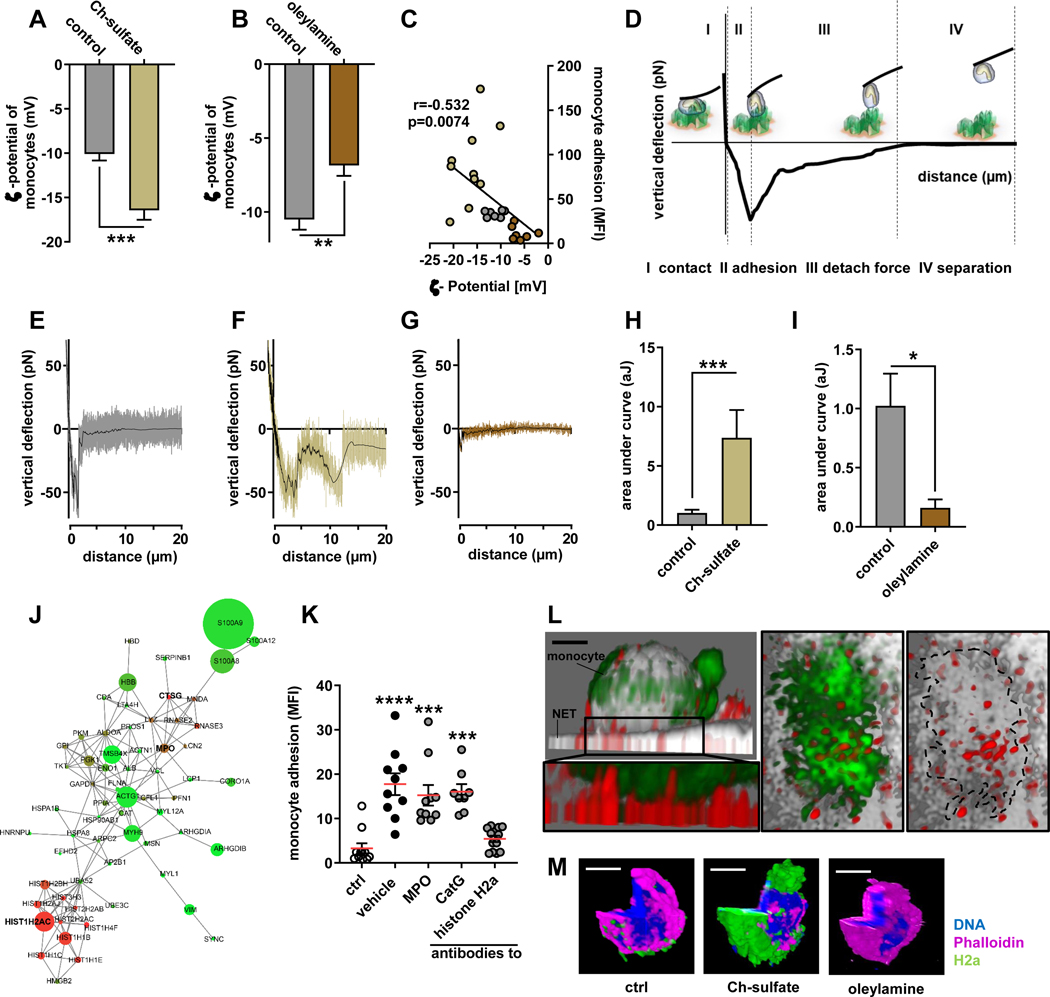
Figure 3: Monocyte adhesion to NETs in regulated by cationic histone H2a.
(A/B) ζ-potential analysis of isolated monocytes treated with Ch-sulfate (A) or oleylamine (B). (C) Pearson correlation of monocyte adhesion to NETs versus monocyte ζ-potential. (D) Scheme of single cell atomic force microscopy (AFM) force spectroscopy. Monocytes were probed on expelled NETs at 200 pN contact force. (E-G) Representative force curves of native monocytes (E) or monocytes treated with Ch-sulfate (F) or oleylamine (G) probed on NETs. (H/I) Quantification of the area under the curve reflecting the energy required to rupture the monocyte-NET interaction. (J) Proteome analysis of NET resident proteins. Circle size reflects protein abundance, while color codes for charge (red cationic, green anionic). (K) Monocyte adhesion to NETs pre-incubated with antibodies to indicated NET-associated proteins. (L) Representative immunofluorescence confocal microscopy image showing the tight interaction between NET resident histone H2a and a NET-bound monocyte, scale bar 3 μm. Displayed is a xy projection (DNA gray, monocyte green, histone H2a red) and a zoom-in underneath (monocyte green, histone H2a red). The right two panels represent a top view (xz) of the zoom-in area thus visualizing the interface between the monocyte (green) and NET-resident histone H2a (red). In the right panel the monocyte is outlined (dashed line). (M) Representative confocal microscopy images of histone H2a binding monocyte in a charge dependent-manner, DNA blue, monocyte purple, histone H2a green, scale bar 5 μm. Data are analyzed by unpaired t-test (A, B, H, I) or Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (K); *p≤0.05, **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001. All data are presented as mean±SEM. HNP, human neutrophil peptides; MPO, myeloperoxidase; PR3, proteinase 3; NE, neutrophil elastase; CatG, cathepsin G.