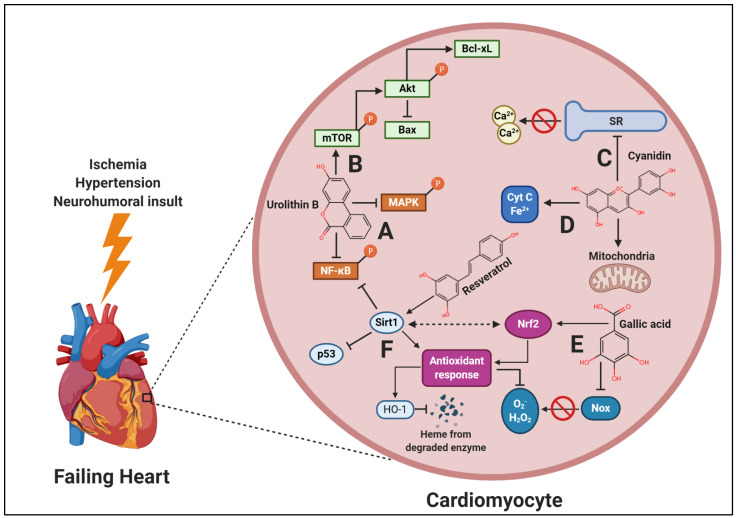
Figure 1.
Mechanisms by which polyphenols, derived from plant-food consumption, may attenuate heart failure (HF). Under chronic, pathological conditions, HF occurs due to a variety of compensatory cellular processes. Polyphenols have many overlapping targets which can attenuate these processes in the following manner: (A) polyphenols, such as the ellagic acid metabolite urolithin B, reduce inflammation by decreasing nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphorylation, preventing pro-apoptotic signaling and inflammatory cytokine release; (B) polyphenols also increase mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and Akt, which reduces autophagy, apoptosis, and bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) while increasing B-cell lymphoma extra-large protein (Bcl-xL); (C) Ca2+-dependent and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, calpain and calcineurin activity are attenuated by polyphenols, such as the anthocyanin cyanidin, and Ca2+ sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) leak is reduced, thus normalizing cellular Ca2+ flux; (D) polyphenols act as substrates of the electron transport chain (ETC), improving ETC efficiency. They also increase the reductive state of cytochrome C (Cyt c) and prevent mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening, maintaining membrane polarization; (E) polyphenols, such as the phenolic acid gallic acid, reduce NADPH-oxidase (Nox) expression and increase antioxidant and detoxifying enzyme activity. This occurs due to increased nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) nuclear translocation, as well as increased crosstalk between Sirt1, leading to attenuation of excessive reactive oxygen species and free heme, thus, oxidative stress and cytotoxicity is reduced. Lastly, (F) sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) is upregulated by polyphenols, such as the stilbene resveratrol, and also by Nrf2 activity which correspondingly increases endogenous antioxidant activity, inhibits pro-apoptotic p53, and inhibits inflammatory signaling of the NF-κB complex via deacetylation. Cumulatively, these multiple and overlapping targets of polyphenols present a potential therapeutic treatment of HF using a plant-based diet. Created with BioRender.com.