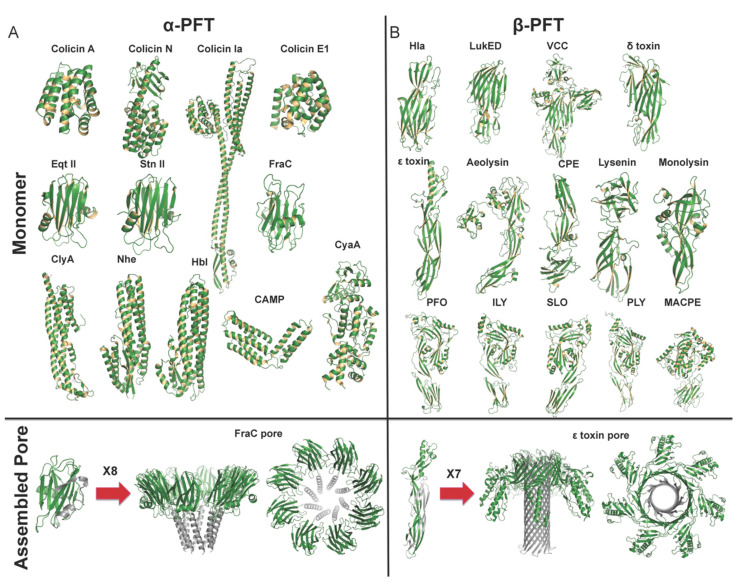
Figure 1.
Structural characteristics of pore-formation specific for each structural family. Representative monomer and pore structure of α-PFTs and β-PFT members are illustrated. For α-PFTs, upon binding to the membrane, α-helices undergo a conformational change to insert into the membrane and form membrane pore. For β-PFTs, monomer β-PFT first assembles in a pre-stem loop, and inserts into the membrane to form a partial β-barrel, and then combines with the other protomers to form a complete β-barrel. (A). α-PFTs: soluble and membrane pore complex, adopted from PDBs 1COL, 1A87, 1CII, 2I88, 1IAZ, 1GWY, 4TSL, 1QOY, 4K1P, 2NRJ, 6JLC, 2COL, 4TSY. (B). β-PFTs: soluble and membrane pore complex, adopted from PDBs 4YHD, 4Q7G, 1XEZ, 2YGT, 1UYJ, 3C0M, 3ZIW, 3ZXD, 4MKO, 1PFO, 1S3R, 4HSC, 5AOF, 2QP2, 6RB9.