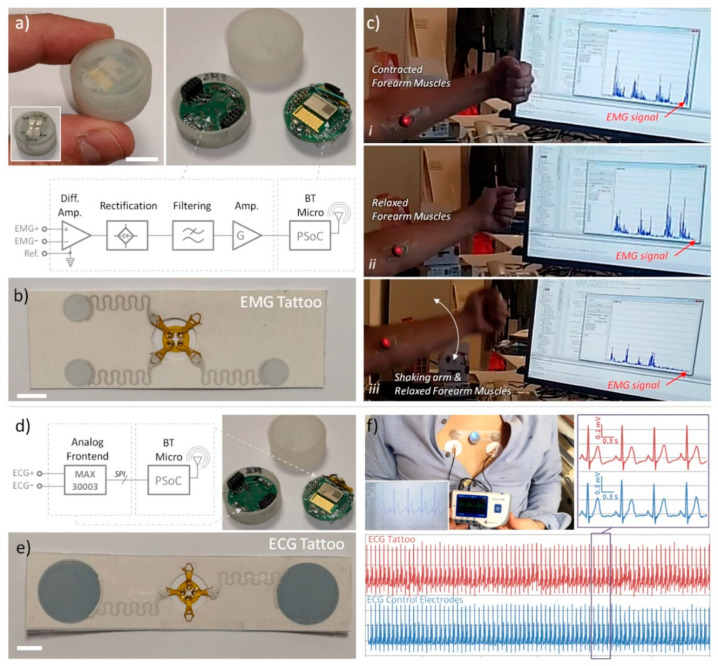
Figure 4.
(a) Picture and schematic of magnetic dockable BT acquisition device, specifically designed to acquire filtered EMG signal (scale bar 1 cm). (b) Picture of three-electrode tattoo for EMG signal acquisition (scale bar 1 cm). (c) Example of use of tattoo EMG electrodes with BT device transmitting low-pass filtered data to a PC, demonstrating large immunity from motion artefacts: signal is generated exclusively by muscle contraction, not from forearm shaking. (d) Picture and schematic of magnetic dockable BT acquisition device, specifically designed to acquire ECG signal. (e) Picture of two-electrode tattoo for ECG signal acquisition (scale bar 1 cm). (f) Measurement of ECG carried out by using tattoo ECG electrodes with specific ECG BT device compared with commercial handhold device using three standard pre-gelled electrodes: rescaled graphs are compared in the same time framework; in the inset, the zoomed view of a small portion (3 s) of the full acquisition time (60 s) is reported. The matching is almost perfect.