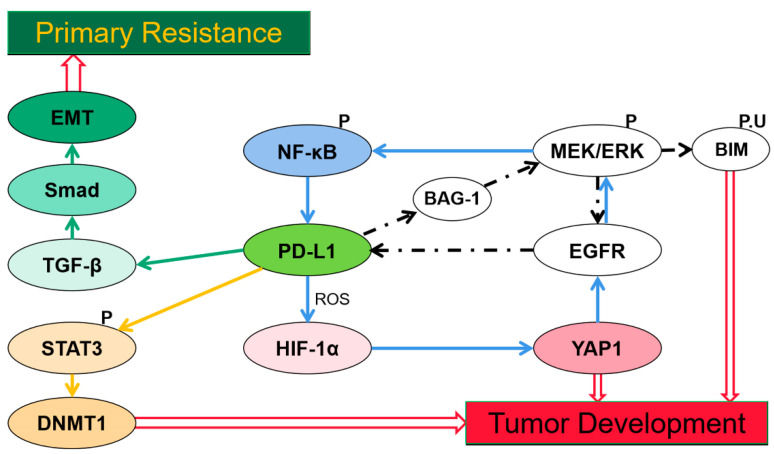
Figure 1.
Signaling pathways and factors involved in programmed cell death ligand-1(PD-L1)-induced resistance. (1) PD-L1 expression induced by epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation activation via extracellular single-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling, indirectly promotes expression of Bcl-2-associated athanogene-1 (BAG-1), the EGFR/ERK/PD-L1/BAG-1 feedback loop reaches the reactivation of ERK signaling which promotes Bcl-2-interacting mediator of cell death (BIM) phosphorylation to help cells escape from apoptosis. (2) PD-L1-induced hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) expression is stimulated by reactive oxygen species (ROS), hypoxia increases YAP-1 expression which confers resistance via a YAP1/EGFR/ERK/NF-κB loop. (3) PD-L1 regulates DNA methyltransferase 1(DNMT1) via Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling and thus induces DNMT1-dependent DNA hypomethylation which promotes cancer development. (4) Activation of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β)/Smad pathway induced by PD-L1 is crucial in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) expression which leads to resistance to TKIs.