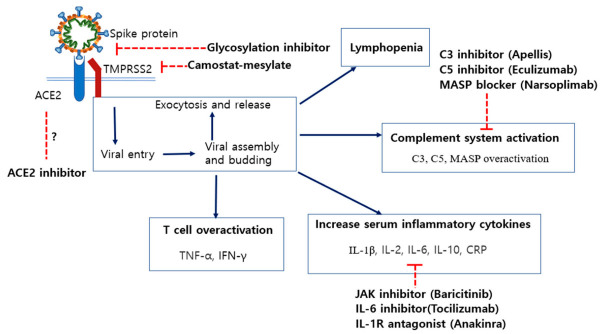
Figure 7.
Possible treatment strategies for COVID-19 patients that block receptor recognition or inhibit immune reactions. Spike protein cleavage is essential for ACE2 recognition. The synthetic serine protease inhibitor, camostat–mesilate, seems to block viral entry by inhibiting the activity of TMPRSS2. Additionally, several glycosylation sites of the spike protein could be targets to lower the affinity of the spike protein for ACE2. Thus, specific glycosylation inhibitors could be an option for COVID-19 treatment. Severe inflammation causes pneumonia, critical tissue injury, or even cytokine storms in COVID-19 patients. Therefore, proven immunomodulators, including the JAK inhibitor baricitinib, the IL-6 inhibitor tocilizumab, or the IL-1R antagonist anakinra, could be beneficial treatments. Additionally, complement system inhibitors are expected to alleviate inflammation and overactivation of immune cells. Several clinical trials are ongoing and further study is needed to ensure their efficacy and safety.