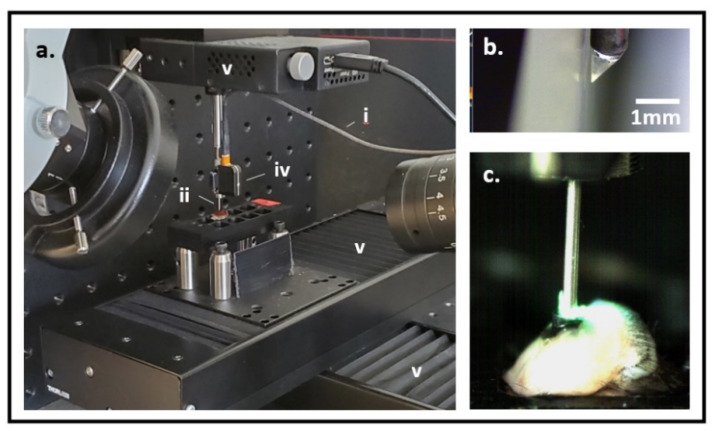
Figure 2.
(a) Experimental set-up for live tissue fluorescence imaging. An optical fiber (i) delivers light excitation through a gradient index (GRIN) lens imaging probe (ii) into a tissue sample (not shown). The resultant fluorescent signal is captured by an external charge-coupled device (CCD) optical detector (iv) for 2-color fluorescence imaging. 4-axis (x, y, z linear and rotational) stage system (v) allows precise positioning of the imaging probe within the tissue sample. (b) GRIN lens imaging probe tip with triangular prism for side-viewing. (c) Imaging probe is placed through the microdevice into live murine tumoral tissue to image fluorescent drug and assay signal.