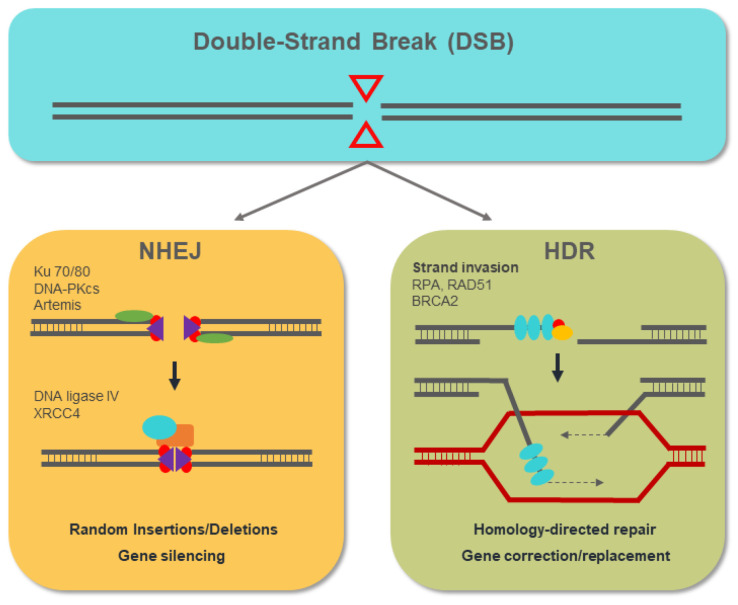
Figure 5.
The non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) mechanism involves the action of the proteins ku70/80, DNA-PKcs, and Artemis, with the ability to bind to the free DNA ends that are generated. The resected DNA ends are joined by the action of ligase IV with the insertion of a variable number of nucleotides (indels) that, in most cases, lead to the generation of null alleles. The homology-directed repair (HDR) pathway begins with the resection of the released DNA ends. The RPA, Rad51, and BRCA2 proteins act by binding and protecting the ssDNA that is generated. Through homologous recombination, the HDR pathway allows the introduction of DNA templates from exogenous donors at the double-strand break (DSB) site, replacing the target genomic sequence.