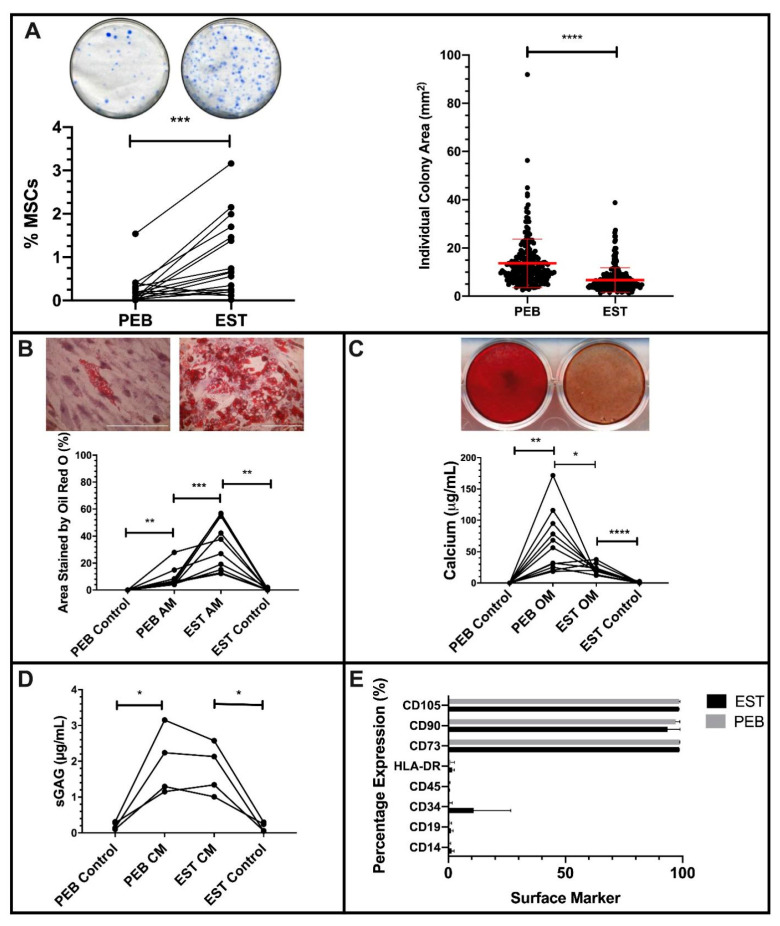
Figure 1.
Characterization of peri-entheseal bone (PEB) and entheseal soft tissue (EST) mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Colony Forming Unit Fibroblast (CFU-F) ((A), Paired t-Test, n = 16) of PEB and EST MSCs shows a significantly higher CFU-F capacity of EST compared to PEB. Individual colonies are also significantly larger in PEB MSCs compared to EST MSCs (Mann–Whitney U Test). ESTs produce significantly more adipocytes than matched PEB MSCs after Oil Red O staining ((B), repeated measures (RM) One-Way ANOVA with Tukey Post-Hoc Test, n = 10). Alizarin red staining ((C), RM One-Way ANOVA with Tukey Post-Hoc Test, n = 11) of osteogenically differentiated PEB and EST MSCs show that matched PEB MSCs produce significantly more calcium than matched EST MSCs. There was no significant difference in the chondrogenic differentiation between PEB and EST MSCs ((D), RM One-Way ANOVA with Tukey Post-Hoc Test, n = 4). Both culture expanded PEB and EST MSCs (n = 3) were positive for MSC lineage markers and were negative for the hematopoietic lineage markers (E). Error bars = mean ± SD * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001 and **** = p < 0.0001. Scale bar = 100 µm. AM = adipogenic media, CM = chondrogenic media, and OM = osteogenic media.