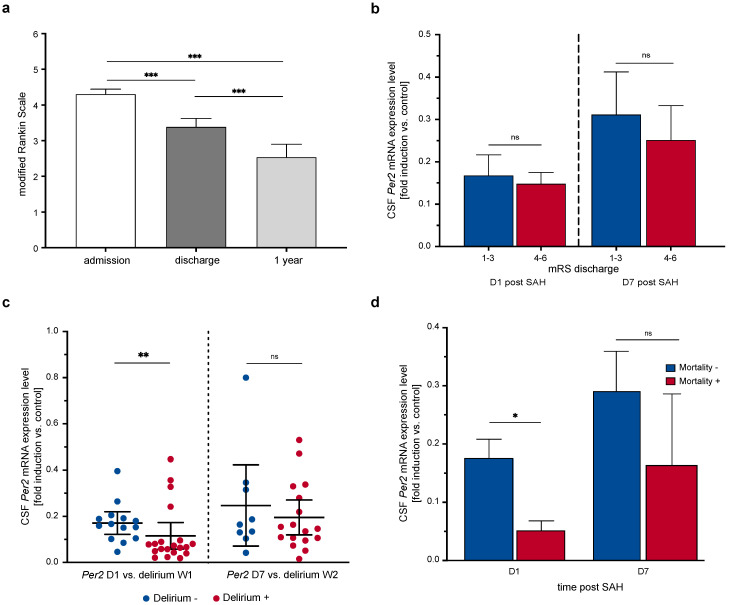
Figure 4.
Extent of early CSF Per2 suppression is associated with delirium and early mortality, but not functional outcome. (a) Functional short- and long-term improvement after SAH reflected in mRS scores at admission, discharge from hospital and 1 year after the SAH event (p < 0.0001, F (1.221, 51.28) = 29.19, n = 37). (b) CSF Per2 expression levels did not differ between patient groups with favorable (mRS 1–3, n = 23)) and non-favorable (mRS 4–6, n = 20) clinical outcome at discharge from hospital (day 1: p = 0.704, day 7: p = 0.557). (c) Early, but not late delirium was associated with higher CSF Per2 expression (p = 0.008, n = 34). (d) Short-term mortality was associated with lower CSF Per2 expression levels on day 1, but not day 7 after SAH (day 1: p = 0.017, n = 43 (n = 37 survivors), day 7: p = 0.676, n = 37 (n = 35 survivors). CSF: cerebrospinal fluid, mRS: modified Rankin Scale, Per2: Period-2, SAH: subarachnoid hemorrhage, W: week. Data presented as mean + SEM/mean ± 95% confidence interval (c), * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.