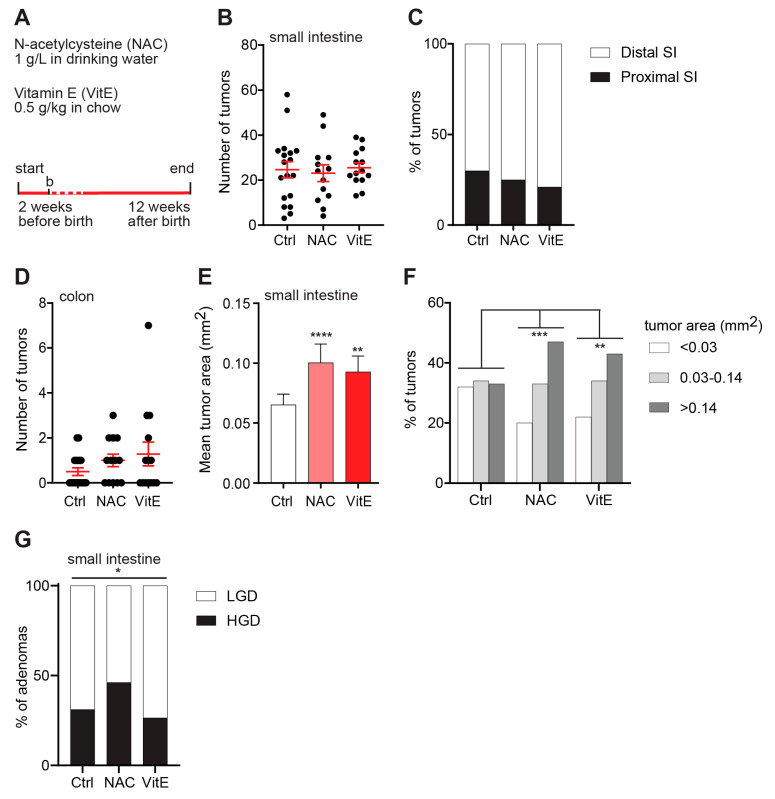
Figure 2.
NAC or vitamin-E treatment increases the size of early tumors. (A) Schematic of the study design. Two structurally unrelated dietary antioxidants, NAC and VitE, were supplemented in the drinking water or chow diet of pregnant dams from two weeks before birth until weaning and, thereafter, to the pups until 12 weeks of age. Dashed line indicates breast feeding period. (B,C) Tumor numbers in one sagittal section of the small intestine (B) and the distribution of tumors between the proximal and distal parts of the small intestine (C) of 12-week-old APCMin/+ mice (n = 18 Ctrl, 13 NAC, 14 VitE). (D) Number of colonic tumors in 12-week-old APCMin/+ mice (n = 18 Ctrl, 13 NAC, 14 VitE). (E,F) The geometric mean area (E) and size distribution (F) of tumors in the small intestines of 12-week-old APCMin/+ mice (n = 303-427 tumors, error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals). (G) Distribution graph showing the percentage of adenomas with HGD or LGD in the small intestines of 12-week-old APCMin/+ mice (n = 74-102 adenomas per group). HGD, high-grade dysplasia; LGD, low-grade dysplasia. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001.