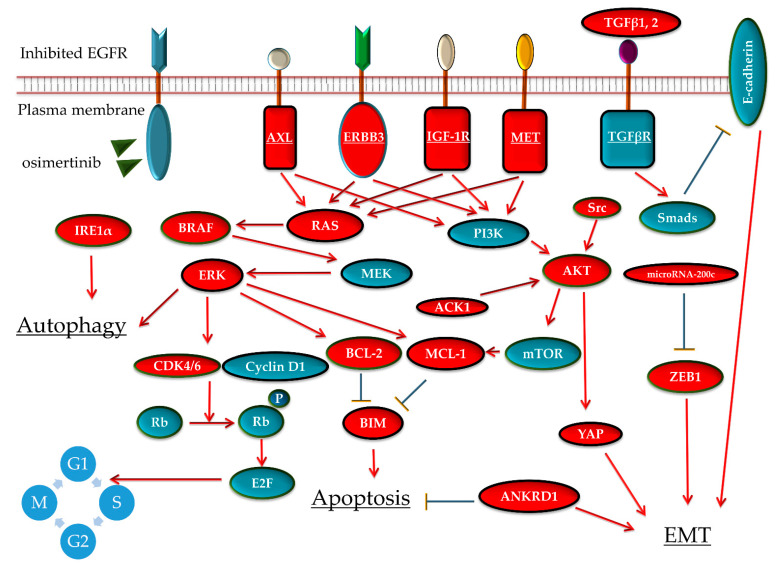
Figure 2.
Scheme of the signal pathway and molecules that reportedly cause osimertinib resistance—AXL [39,41,52], HER3 [45], IGF1R [51,57], MET [33,52], TGFβ1 [40], TGFβ2 [59], BRAF [43], RAS [32,35], ERK [37], Src-AKT [35], ACK1 [48], CDK4/6 [55], BCL-2 [56], MCL-1 [34], BIM [34,50], YAP [54], ANKRD1 [36], microRNA-200c [46], ZEB1 [46,58], and IRE1α [38] (highlighted in red)—in cell line models treated with osimertinib. EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; AXL, AXL receptor tyrosine kinase; ERBB3, human epidermal growth factor receptor-3; IGF1R, insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; MET, MET proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase; TGF, transforming growth factor; ACK1, activated Cdc42-associated kinase-1; CDK4/6, cyclin-dependent kinase; BCL-2, B-cell lymphoma-2; YAP, yes-associated protein; ANKRD1, ankyrin repeat domain-1; IRE1α, inositol-requiring enzyme-1α.