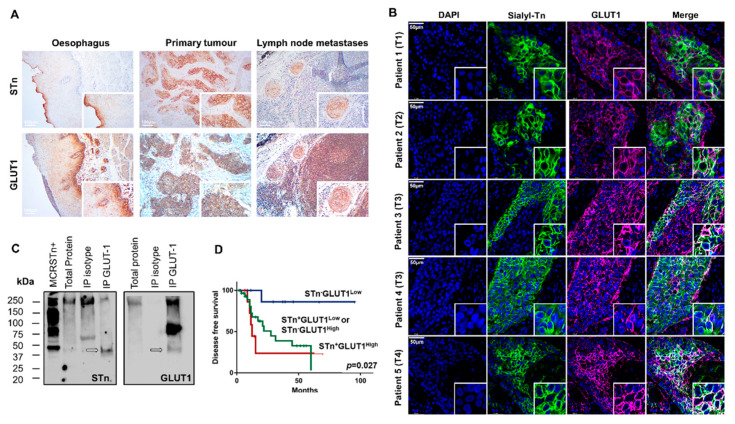
Figure 4.
GLUT1-STn is widely expressed in ESCC and correspondent metastases and associates with decreased disease-free survival. (A) GLUT1 and STn are co-localized in the same tumor areas in primary tumors, lymph node metastases but not in the healthy esophagus. The immunohistochemistry analysis panels show the co-expression of GLUT1 and STn in the same areas in tumors and lymph node metastases strongly suggesting GLUT1-STn glycoforms. Immunohistochemistry of the healthy esophagus suggests that these epitopes are present in different areas. (B) GLUT1 and STn are expressed in the same cancer cells in all studied tumors. Double immunofluorescence for GLUT1 and STn show co-localization in the same cells in all studied tumors, across different stages and histopathological natures of the disease. Nuclei stained in blue; STn in green; GLUT1 in purple; Co-expression (white). (C) Western blot confirms the existence of GLUT1-STn glycoproteoforms. GLUT1 was immunoprecipitated from ESCC and blotted for both GLUT1 and STn. Isotype immunoprecipitated proteins were used as negative controls. MCRSTn+ bladder cancer cell line was used as positive control for STn expression. All blots showed bands at 250 kDa and above most likely resulting from unspecific co-precipitation of mucins carrying STn. On the other hand, GLUT1 blots evidence a major band just above 75 kDa not present in STn blots. A less intense band at approximately 50 kDa was observed in both GLUT1 and STn blots reinforcing the existence of GLUT1-STn. (D) GLUT1-STn overexpressing tumors present reduced decreased survival when compared to tumors showing no STn expression or high STn expression and decreased levels of GLUT1.