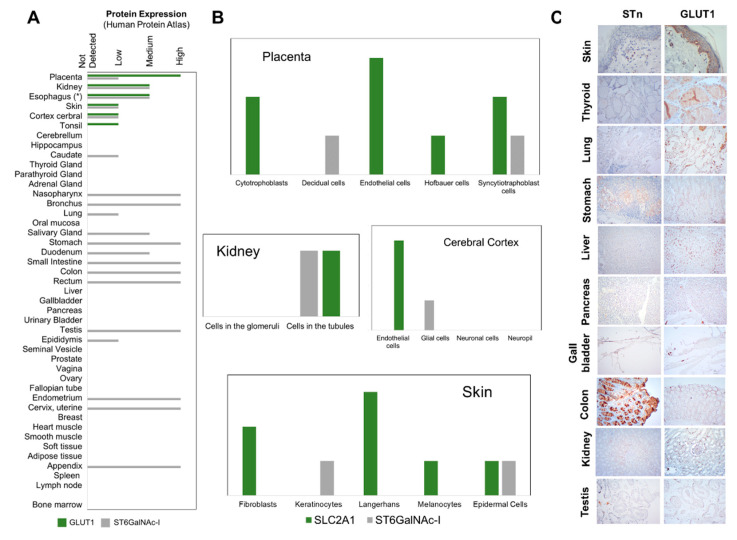
Figure 5.
STn and GLUT1 expressions are rarely overlapping in healthy tissues. (A) GLUT1 and ST6GalNAc I (a key glycosyltransferase for STn biosynthesis) expressions in healthy human tissues. According to the Human Protein Atlas, GLUT1 and ST6GalNAc I are co-expressed in the placenta, kidney, skin and the cerebral cortex, suggesting potential to express GLUT1-STn. GLUT1 for the esophagus concerned experimental data from the present report, according to Figure 4A. (B) GLUT1 and ST6GalNAc I expressions in different cell types of the placenta, kidney, cerebral cortex and skin. Syncytiotraphoblast cells of the placenta, cells in the kidney tubules and epidermal cells of the skin co-express GLUT1 and ST6GalNAc I, supporting capacity to present GLUT1-STn. (C) GLUT1 and STn expressions in the skin, thyroid, lung, stomach, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, colon, kidney, testis. GLUT1 was detected at the cell membrane in the immune cells’ component of the stomach, liver, colon, lung and pancreas. STn was found mostly in the cytoplasm and, to less extent, the membrane of parietal and goblet cells of the respiratory and digestive tracts. No evidence supporting co-expression in the same areas were found.