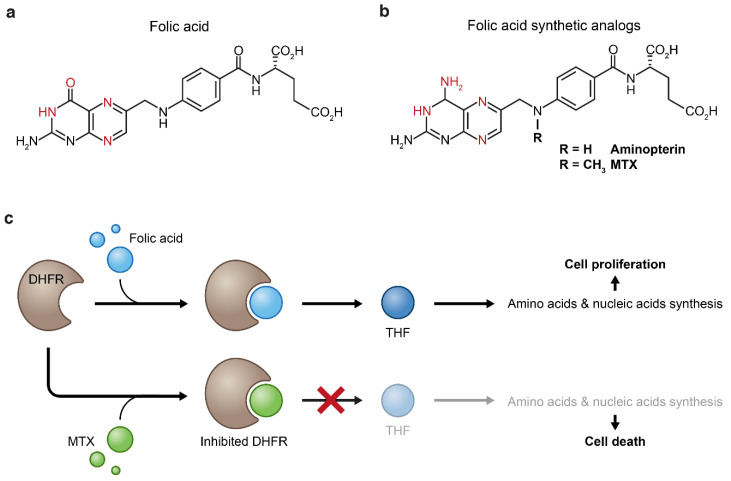
Figure 4.
Folic acid (a) and its synthetic analogs (b). Both folic acid and its analogs bind to dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) through formation of hydrogen bonds (the atoms that form these bonds are in red). Replacement of the enol group of folic acid by an amine group results in increased binding affinity of the synthetic analogs to the DHFR enzyme which inhibits the biosynthesis of tetrahydrofolate (THF) (c). Tetrahydrofolate starvation causes impaired cellular anabolism which eventually leads to cellular death.