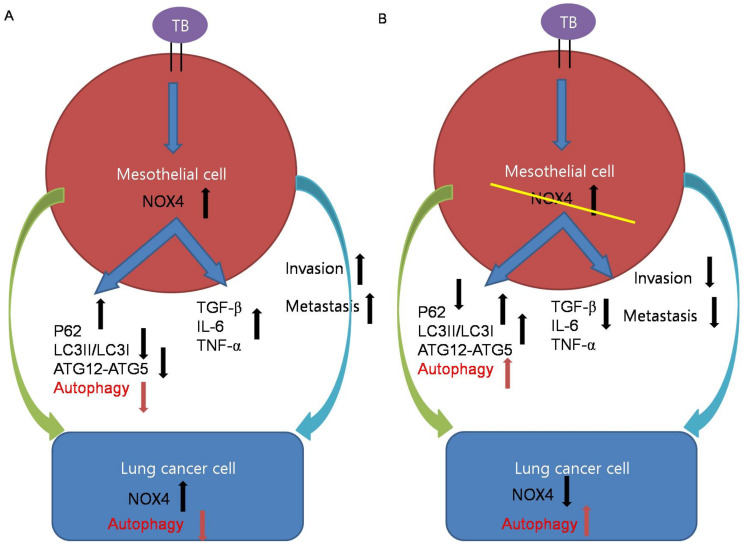
Figure 6.
Schematic illustrations of the mechanism by which tuberculous fibrosis contributes to the malignant potential of lung cancer. (A) TB-infected PMCs exhibited increased expression of NOX4. NOX4 downregulates autophagy signaling and induces TGF-β, IL-6, and TNF-α, leading to cancer cell proliferation. In lung cancer cells after exposure to TB-infected PMCs, NOX4 signaling increases and autophagy signaling decreases. (B) Knockdown of NOX4 in TB-infected PMCs increases autophagy signaling and reduces TGF-β, IL-6, and TNF-α, leading to cancer suppression.