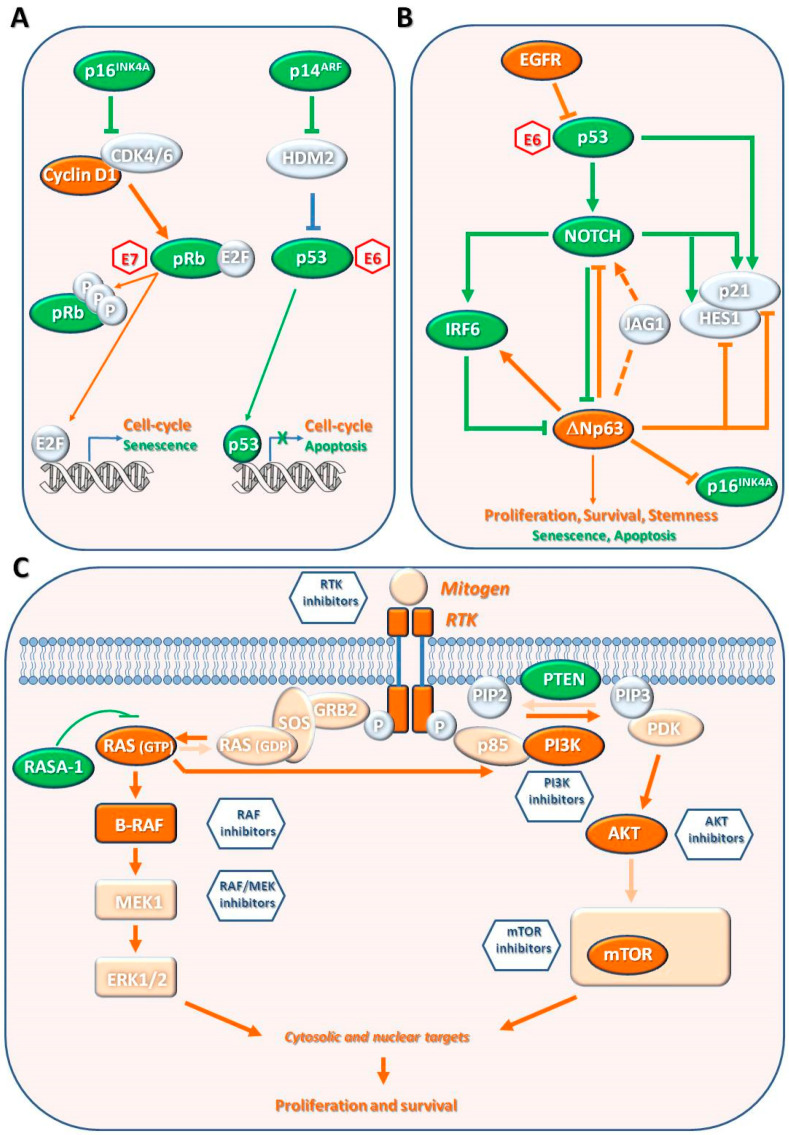
Figure 6.
Pathways involved in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) pathogenesis. Molecular alterations, which drive cSCC development, have been identified in pathways involved in cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, senescence, differentiation, and mitogenic/survival. (A) The tumor suppressor genes p16INK4A and p14ARF control retinoblastoma (pRb) and p53 pathways, respectively. Their loss of function promotes cell cycle counteracting senescence or apoptosis. Aberrant activation of E2F transcription can also be due to cyclin D activation or pRb expression loss. pRb and p53 inactivation is also mediated by E6 and E7 (red hexagons) human papilloma virus (HPV) proteins. (B) EGF-R aberrant activation, p53 inactivation, or NOTCH gene mutations inactivate the NOTCH pathway. Inactivation of NOTCH abolishes the direct or IRF6-mediated suppression of ΔNp63, favoring proliferation, survival, and stemness. NOTCH inactivation also counteracts senescence and apoptosis mediated by its targets (HES1 and p21). Moreover, ΔNp63 upregulation represses the expression of HES1, p21, and p16INK4A. (C) RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways share the up-stream proteins, such as tyrosine kinase receptors (RTK) and RAS. Activating mutations in RTK, RAS or inactivation of negative regulator RASA1 promotes cell proliferation and survival through constitutive activation of both pathways. Aberrant activation of these pathways can also derive by B-RAF or PI3K/AKT activation, or Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) inactivation. The RTKs and the downstream pathways can be targeted with several drugs (blue hexagons) to inhibit cSCC progression. However, both pathways can be activated by RAS mutations, present in photodamaged skin, as part of a compensatory mechanism that could drive resistance to therapeutic targeting strategies. Proteins with commonly accepted tumor promoting and suppressing functions are highlighted in orange and green, respectively. Activated or downregulated processes (circles, squares and arrows) are highlighted in dark orange and green, respectively. Block and dash arrows indicate direct or indirect interactions, respectively.