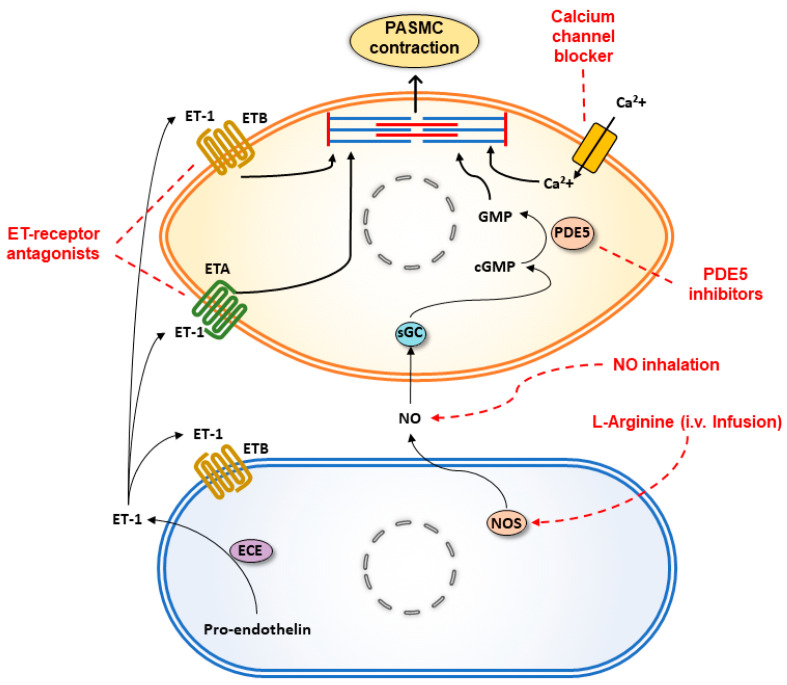
Figure 3.
Targets of potential pharmacological agents to prevent or reverse HPV. Upon exposure to hypoxic condition, in pulmonary artery endothelial cells (PAECs), endothelin converting enzyme (ECE) increases endothelin-1 (ET-1) levels, which in turn causes pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell (PASMC) contraction via ET-1 A and B receptors (ETA and ETB). ETA and ETB can be blocked by endothelin receptor antagonists such as bosentan to inhibit hypoxia induced PASMC contraction. Similarly, nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity is also impaired in hypoxic PAECs, leading to decreased levels of nitric oxide (NO). Further, decreased bioavailability of NO for the activity of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) results in decreased levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in PASMCs and PASMC contraction. NO level can be restored by either infusion of L-arginine, which is used by NOS as a substrate, or by NO inhalation, which directly activates sGC. To prevent cGMP degradation in PASMCs, phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) can be inhibited by PDE5 inhibitors such as sildenafil and tadalafil. In addition, calcium influx and PASMC contraction can be inhibited with calcium channel blockers such as nifedipine.