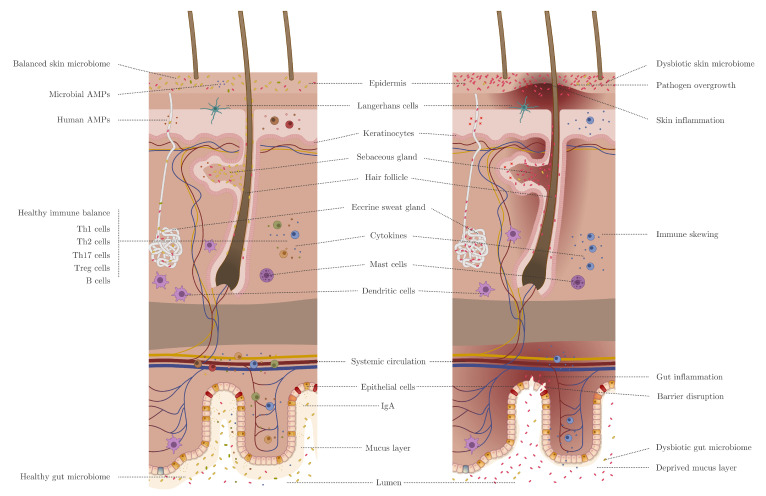
Figure 1.
Inflammatory and microbial influences between the gut and skin for a healthy state (left) and a dysbiotic state (right): The intestinal and epidermal barriers are connected through the systemic circulation (blood and lymph) and are visualized here together in a simplistic manner. The dysbiotic state is characterized by an impaired gut barrier (imbalance in gut microbiome, reduced mucus layer, reduced IgA secretion, barrier disruption, intestinal permeation into the bloodstream, and gut inflammation) and an impaired skin barrier (imbalance in skin microbiome, reduced human and microbial antimicrobial peptides (AMP) production, skin rashes/thickening/lesions, and skin inflammation). Gut and skin dysbiosis are connected through an immune imbalance (Th2 skewing in this example), whereas crosstalk can be bidirectional.