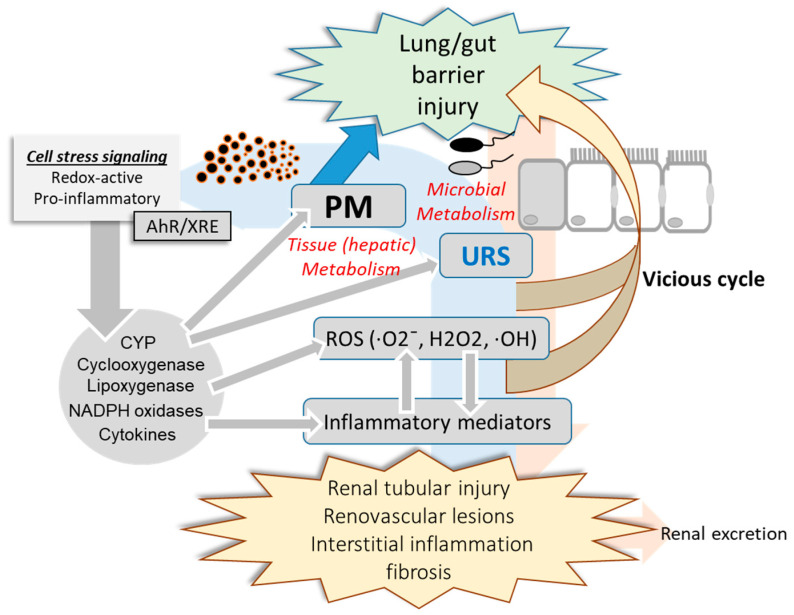
Figure 3.
PM-induced alteration in mucosa-kidney axis. PM-insulted mucosal barrier allows the translocation of PM, uremic retention solutes (URS), and their metabolites which can have detrimental effects on the mucosa-kidney axis via stress signaling including AhR-linked pathways. Moreover, invasive microbes and harmful metabolites from the altered microbiota community can contribute to the systemic and renal inflammation during PM exposure. In addition to renal distress, reactive oxygen species (ROS), inflammatory mediators and the circulating xenobiotic agents including PM components and URS injure the mucosal barrier integrity in a feedback way.