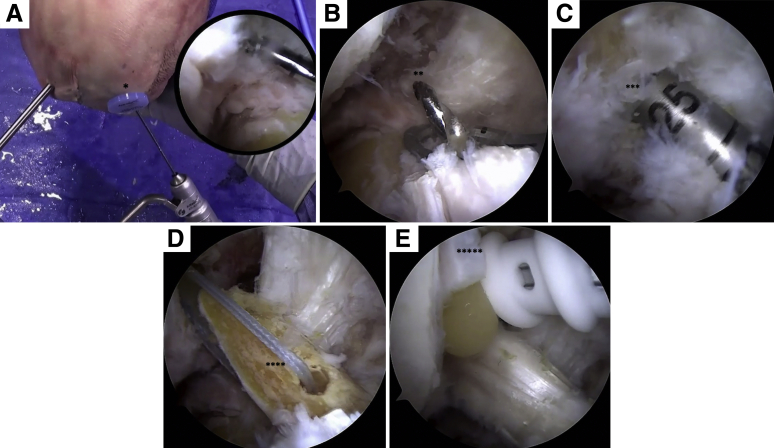
Fig 6.
Arthroscopic view of right knee in flexion. (A) A skin incision is made above the pes anserinus, and a guidewire is passed through the tibial guide just beyond the tibial cortex at the anterior cruciate ligament footprint (asterisk). (B) The tibial tunnel is created using an impaction reamer (asterisks) matching the size of the graft. A transtibial approach is used to create the femoral tunnel using the anterior cruciate ligament remnants at the femoral footprint as a guide. A stab incision is made through the skin at the exit point of the guidewire. (C) The femoral tunnel is reamed to 20 to 25 mm (asterisks). (D) The graft is shuttled from distal to proximal using the lead sutures (asterisks). (E) The button is secured to the cortex; then, a 6-mm interference screw is used to fix the bone plug in the femur (asterisks).