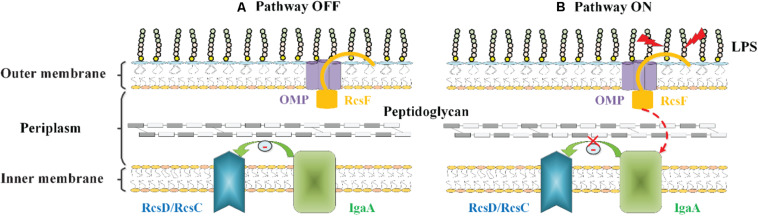
FIGURE 4.
The role of RcsF/OMP complexes in sensing OM stress in E. coli. The OM lipoprotein RcsF is seated in an OMP. Its flexible, lipidated N-terminal domain is surface exposed, probing the state of LPS lateral interactions. The transmembrane segment of RcsF is threaded through the lumen of the OMP exposing the C-terminal domain in the periplasm. (A) In the absence of stress, IgaA inhibits the Rcs signaling, and the Rcs system is deactivated. (B) When LPS lateral interactions are disrupted by cationic antimicrobial peptides, or by the loss of negatively charged phosphate groups on the LPS molecule, this information is transduced to the RcsF C-terminal signaling domain located in the periplasm, resulting in the activation of the Rcs system by an unknown mechanism.