Figure 6.
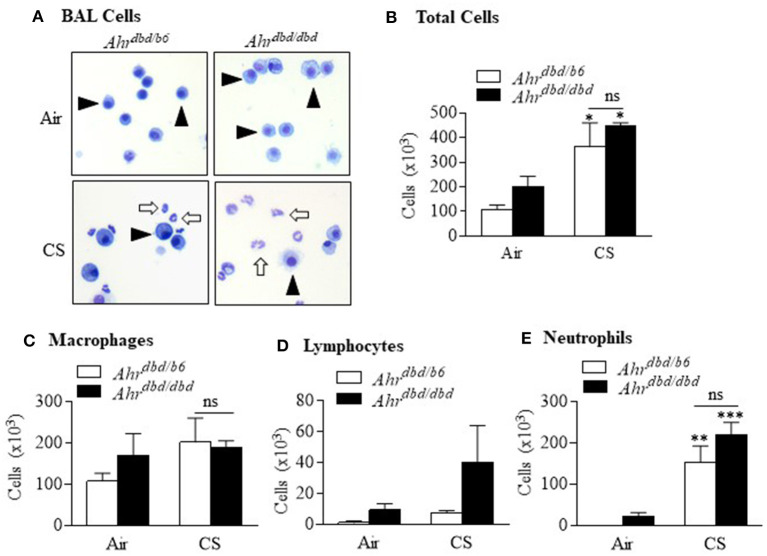
Suppression of sub-chronic cigarette smoke exposure is DRE-independent. Ahrdbd/b6 and Ahrdbd/dbd mice were exposed to CS or room air for 2 weeks and differential cell counts in the BAL performed. (A) BAL cells—there was a noticeable increase in the presence of neutrophils (open arrows) after CS exposure (arrowheads indicate macrophages). (B) Total cells—there was a significant increase in the total number of cells in the BAL after CS exposure (*p < 0.05 compared to respective air exposed group). There was no significant difference in cells between CS-exposed Ahrdbd/b6 and Ahrdbd/dbd mice (ns = not significant). (C) Macrophages—there was no difference in macrophage numbers between CS-exposed Ahrdbd/b6 and Ahrdbd/dbd mice (ns = not significant). (D) Lymphocytes—while there was a trend toward more lymphocytes in CS-exposed Ahrdbd/dbd mice, this increase did not reach statistical significance. (E) Neutrophils—there was a significant increase in the number of neutrophils in both the CS-exposed Ahrdbd/b6 (**p < 0.01) and Ahrdbd/dbd mice (***p < 0.001) compared to room-air exposed mice. There was no significant difference (ns) in neutrophils between the CS-exposed Ahrdbd/b6 and Ahrdbd/dbd mice. Results are shown as means ± SEM (n = 2–4 female mice per group).