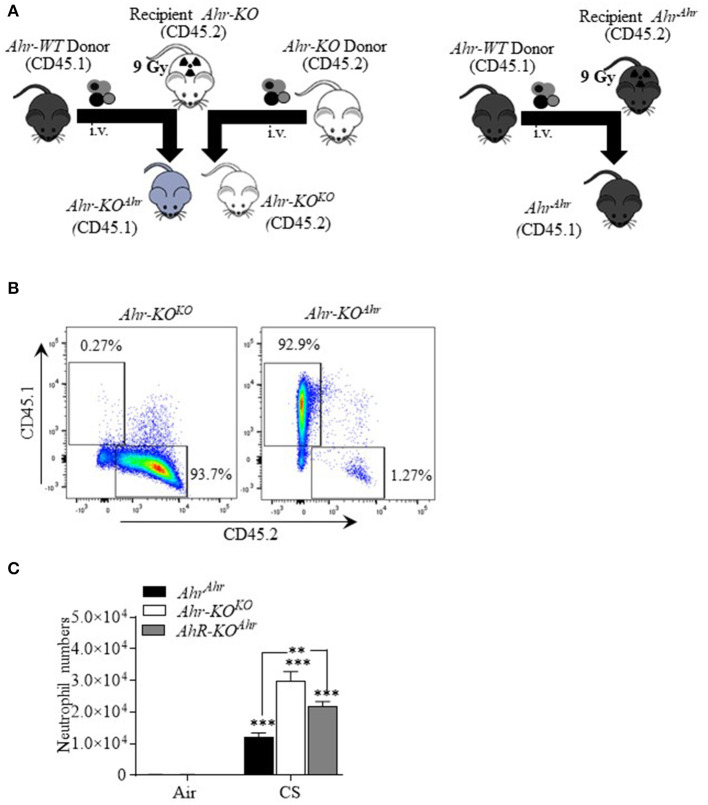
Figure 7.
Suppression of CS-induced neutrophilia by hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic AhR expression. (A) Schematic of bone marrow chimeras: AhR-KO mice (recipient) were irradiated with 9 Gy and bone marrow cells transferred from Ahr-expressing (AhrAhr) mice to create chimeric mice in which the non-hematopoietic (structural) cells are KO but hematopoietic cells have AhR. Control mice (after irradiation of recipient) included AhrAhr (all cells with AhR) and Ahr-KOKO (all cells KO). (B) Flow cytometry of CD45.1 cells: Bone marrow cell subsets from Ahr-KOKO (CD45.2) and BM chimeric mice Ahr-KOAhr (CD45.1) were labeled with antibodies for CD45.1 and CD45.2 and analyzed using flow cytometry. Data presented are representative dot plot. For the Ahr-KOAhr mice, BM cells were entirely donor derived (CD45.1) after reconstitution. (C) BAL neutrophils: acute (3 day) CS exposure significantly increased BAL neutrophils in AhrAhr mice, Ahr-KOKO, and chimeric (Ahr-KOAhr) mice compared to respective air-exposed mice (***p < 0.001). Neutrophils were significantly higher in Ahr-KOKO (**p < 0.01) and Ahr-KOAhr mice (**p < 0.01) compared to AhrAhr mice. There was some reduction in neutrophils in Ahr-KOAhr mice. N = 4–5 male mice per experimental condition.