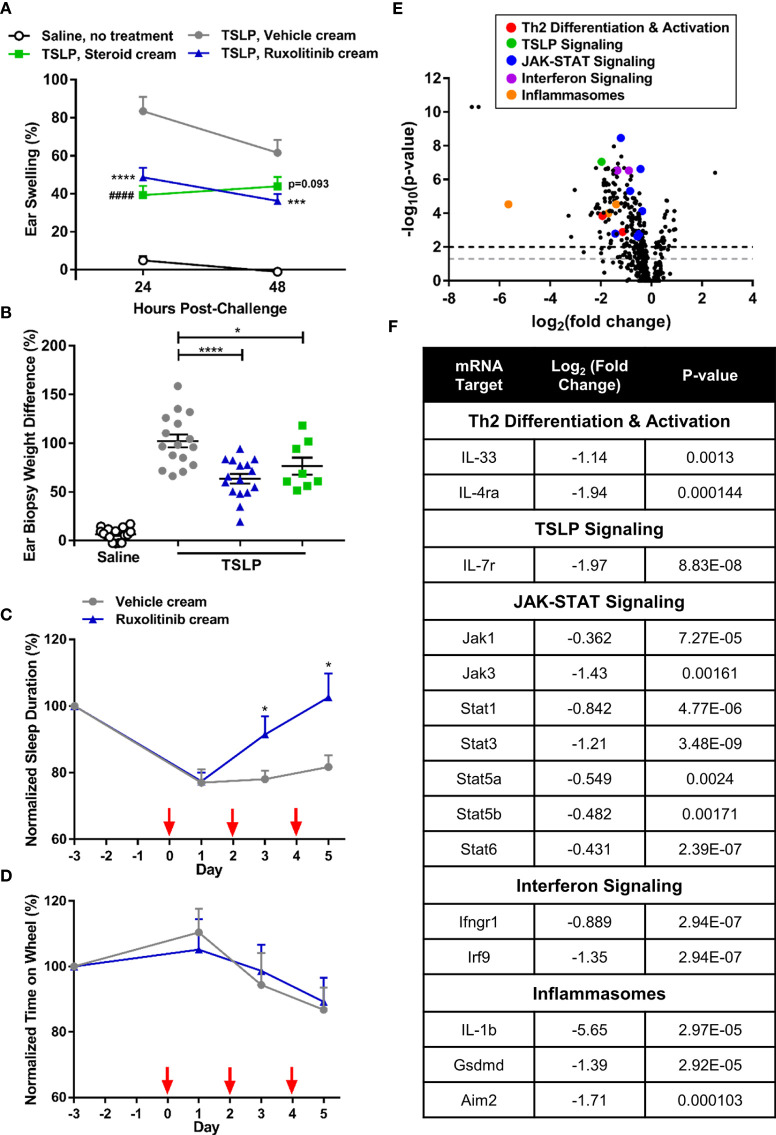
Figure 1.
Ruxolitinib cream decreased inflammation and restored sleep duration in the acute thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP)-induced dermatitis mouse model. (A) Repeated intradermal TSLP challenge induced acute ear swelling, which was significantly abrogated by ruxolitinib cream treatment. (B) Ruxolitinib cream efficacy was confirmed by a significant decrease in ear biopsy weight (% increase between right challenged ear and left control ear) at study termination. N = 16 mice per group. (C) Treatment with ruxolitinib cream restored sleep duration (sum of time points in a 24 h period where detectable motion ≤ 3) to baseline levels without causing sedation (D), as shown by unaltered wheel activity (sum of time spent on wheel during a 24 h period) across groups. Red arrows indicate TSLP immunizations. N = 10 mice per group (C, D). (E) Nanostring ear skin RNA analysis revealed differential gene expression between ruxolitinib cream and vehicle cream (baseline) treatment. Points above the gray and black dashed lines have adjusted p-values <0.05 and <0.01, respectively. (F) Inflammatory genes from multiple pathways were downregulated with ruxolitinib cream treatment. N = 8 mice per group. Data represents mean + SEM. (A) ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, vehicle vs. ruxolitinib. ####p<0.0001, vehicle vs. steroid. (B, C) *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001.