FIG. 1.
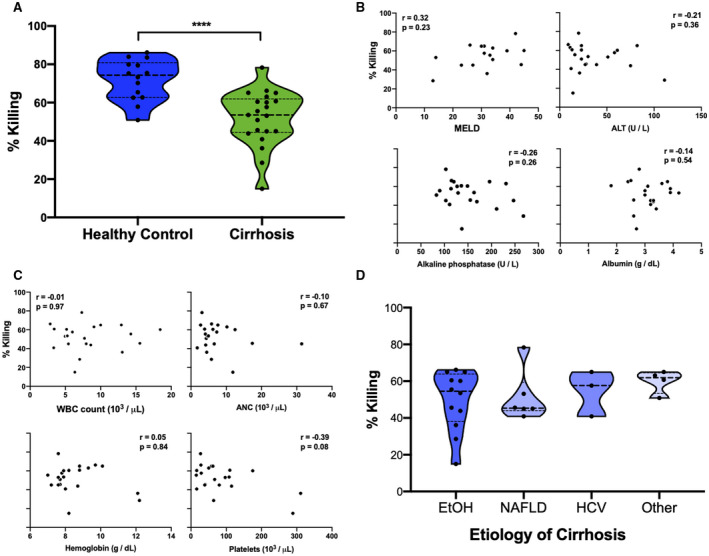
Neutrophils from patients with cirrhosis have a diminished ability kill C. albicans. (A) Neutrophil percent killing of C. albicans is significantly decreased in patients with cirrhosis (n = 21) compared to healthy controls (n = 14). Neutrophil percent killing of C. albicans is not correlated with biochemical measures of liver function, including MELD scores (B), nor WBC count, ANC, Hb, or platelet count (C). (D) Neutrophil percent killing of C. albicans does not differ in patients with alcoholic (EtOH), NAFLD, HCV, or other etiologies of cirrhosis. ****P < 0.0001 (Mann‐Whitney U test). Abbreviation: EtOH, ethanol.
