FIG. 2.
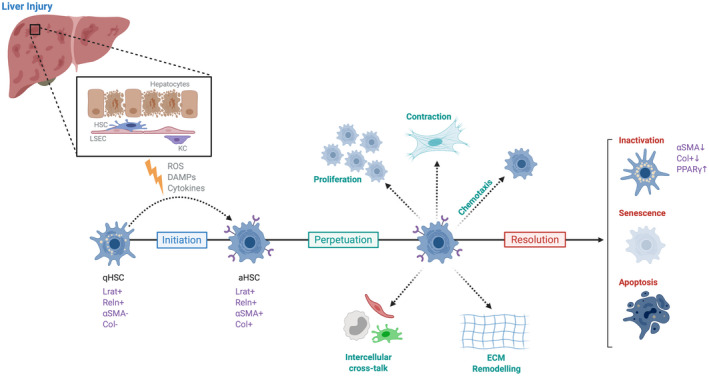
Phases of hepatic stellate cell activation and resolution. Initiation of hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation occurs following liver injury, and is driven by a variety of signals( 19 ) including reactive oxygen species (ROS), damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) and cytokines released from damaged hepatocytes. During the initiation phase, quiescent hepatic stellate cells (qHSCs) transdifferentiate to their activated phenotype (aHSC). The perpetuation phase follows, characterised by a range of HSC phenotypic changes. When injury has subsided, a resolution phase follows, where HSCs undergo apoptosis, become senescent or revert to an inactive phenotype, which is more responsive to subsequent injurious stimuli. Abbreviations: LSEC, liver sinusoidal endothelial cell; KC, kupffer cell; Reln, reelin.
