Figure 3. C‐terminal IDR arginine methylation enhances METTL14–RNA interactions and METTL3/METTL14 RNA methylation activity.
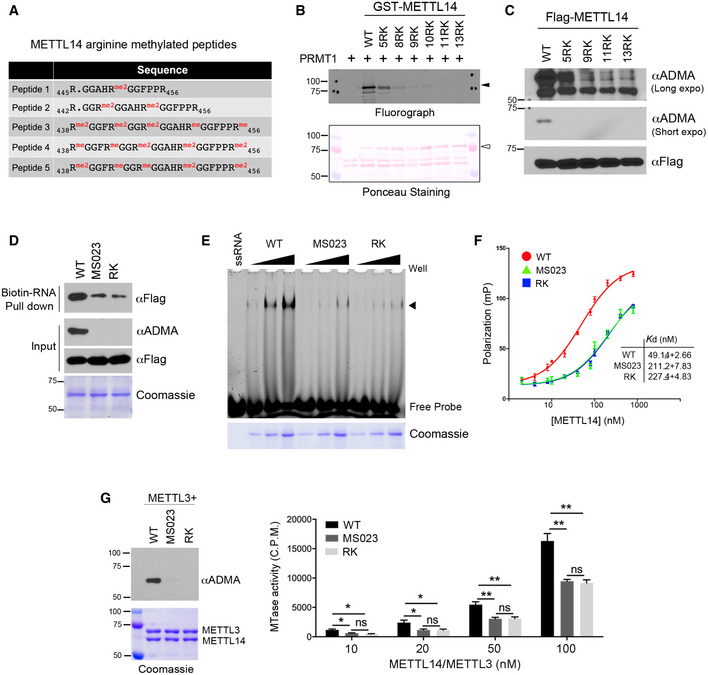
- Summary of METTL14 arginine‐methylated peptides identified by LC‐MS/MS.
- METTL14 IDR arginine methylation occurs at multiple arginine residues within RGG/RG motifs. Mutation of five arginine sites identified from mass spectrometry reduces METTL14 arginine methylation, but only mutation of all arginine residues to lysine completed blocked METTL14 methylation. Ponceau S staining shows the loading of the recombinant proteins. The black triangles indicate arginine methylated‐METTL14; open triangles indicate recombinant METTL14 proteins.
- METTL14 is methylated at multiple arginine residues in cells. HEK293 cells expressing Flag‐tagged WT or various R‐to‐K METTL14 mutants were lysed and immunoprecipitated with an anti‐Flag antibody. Arginine methylation of immunoprecipitated METTL14 was detected by Western blot analysis using an anti‐ADMA antibody. Both short and long exposures of the chemiluminescence signals are shown.
- Arginine methylation of the METTL14 IDR enhances its interaction with RNA substrates. RNA pull‐down assay was performed by incubating biotin‐labeled RNA with WT, hypomethylated (MS023), and arginine methylation‐deficient (RK) mutant METTL14. The pull‐down samples were detected by Western blot analysis using an anti‐Flag antibody. The methylation status of the recombinant proteins was confirmed by Western blot analysis using an anti‐ADMA antibody.
- EMSA was performed to compare the interactions of WT, hypomethylated (MS023), and arginine methylation‐deficient (RK) mutant METTL14 with 6‐FAM‐labeled RNA. Arrow indicates the shift of the RNA probe caused by the protein–RNA interaction. Coomassie staining shows the increasing amounts of recombinant proteins used in the assay.
- Fluorescence polarization assays were performed by incubating 6‐FAM‐labeled RNA with WT, hypomethylated (MS023), and arginine methylation‐deficient (RK) mutant METTL14. Each point represents the average of three independent replicates and error bars represent standard deviation (SD). The dissociation constant values (K d) were listed as mean ± SD.
- Arginine methylation of the C‐terminal IDR enhances the RNA methylation activity of the METTL14/METTL3 complex in vitro. In vitro RNA methylation assays were performed by incubating biotin‐labeled RNA substrates with METTL3/METTL14 methyltransferase complexes containing WT, hypomethylated (MS023), and arginine methylation‐deficient (RK) mutant METTL14 in various concentrations (10–100 nM). The methylation status of the METTL3/METTL14 complex was confirmed by Western blot analysis using an anti‐ADMA antibody. Coomassie staining shows the purification of the enzyme complex. Enzymatic activity was measured in counts per minute (c.p.m.) using a scintillation counter. Data from three replicates were analyzed by Student’s t‐test and shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant.
Source data are available online for this figure.
