Figure 4. Arginine methylation of the C‐terminal IDR enhances the interaction of METTL14 with RNAPII in cells.
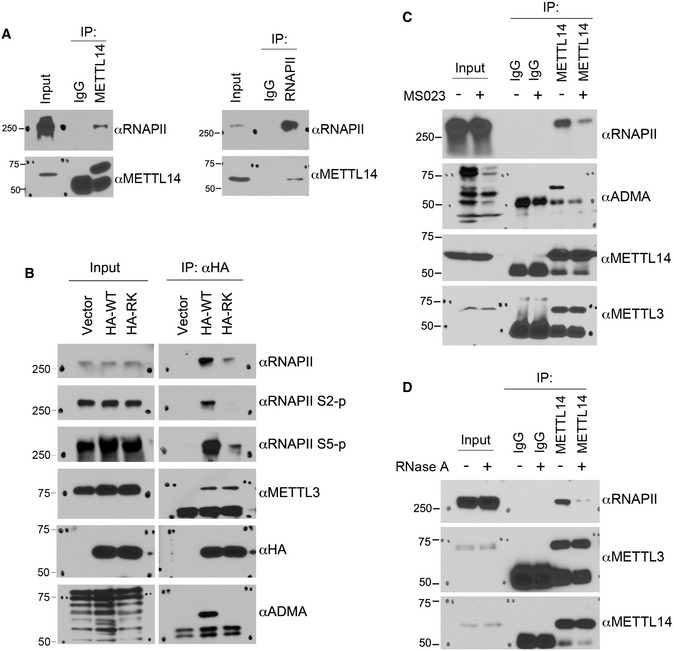
- Endogenous METTL14 interacts with RNAPII. Endogenous co‐immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed using the METTL14 antibody for IP and the RNAPII antibody for Western blot detection (left panel) and using the RNAPII antibody for IP and the METTL14 antibody for Western blot detection (right panel).
- Arginine methylation of the METTL14 C‐terminal IDR enhances its interaction with RNAPII. HEK293 cells were transfected with HA‐tagged WT or arginine methylation‐deficient (RK) mutant METTL14. IP was performed using an anti‐HA antibody, and Western blot analysis was performed using the indicated antibodies.
- Co‐IP assays were performed to compare the interactions between METTL14 and RNAPII in control and MS023‐treated HEK293 cells. Cells were treated with either DMSO or MS023 (1 μM) for 48 h before they were lysed. IP was performed using control IgG and METTL14 antibodies, respectively. Western blot analysis was performed using anti‐RNAPII, anti‐ADMA, anti‐METTL14, and anti‐METTL3 antibodies.
- Co‐IP assays were performed to examine the involvement of RNA in the METTL14–RNAPII interaction. Total cell lysates were either left untreated or treated with RNase A to remove the RNA component before IP. Western blot analysis was performed using anti‐RNAPII, anti‐METTL3, and anti‐METTL14 antibodies.
Source data are available online for this figure.
