Figure 7. Loss of METTL14 arginine methylation sensitizes mESCs to DNA damage.
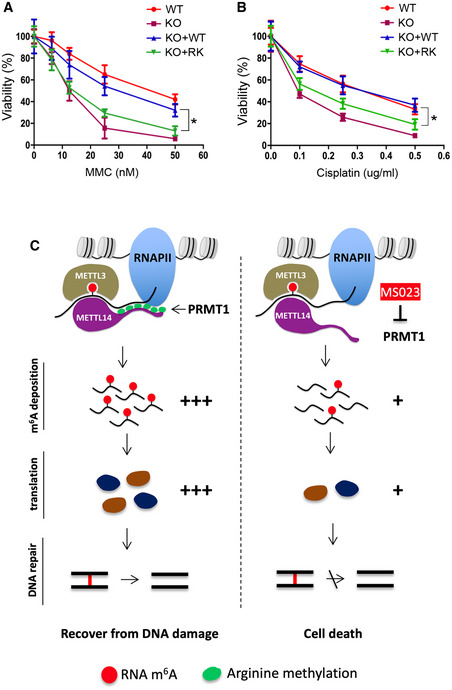
- mESCs expressing arginine methylation‐deficient mutant (RK) METTL14 are sensitive to ICL damage induced by MMC. WT, Mettl14 KO, KO + WT, and KO + RK mESCs were treated with various concentrations of MMC for 4 days before cell viability was measured.
- Similar to (A), except that mESCs were treated with cisplatin, another ICL‐inducing chemical, at various concentrations.
- Proposed model for METTL14 C‐terminal IDR arginine methylation‐mediated regulation of m6A RNA modification and its effects on ICL DNA repair. PRMT1‐mediated arginine methylation of the C‐terminal IDR of METTL14 promotes its interactions with RNA substrates and RNAPII, which enables efficient m6A deposition on transcripts involved in ICL repair. The deposition of m6A enhances the translation efficiency of these DNA repair genes, promoting the recovery of mESCs from DNA damage. Inhibiting METTL14 arginine methylation using the type I PRMT inhibitor MS023 reduces m6A deposition and the protein synthesis of ICL repair genes, thus sensitizing mESCs to DNA damage‐induced cell death.
Data information: In both (A) and (B), each point represents the average of three independent replicates and error bars represent standard deviation (SD). Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t‐test. *P < 0.05.
Source data are available online for this figure.
